The hippo kinase STK38 ensures functionality of XPO1
- PMID: 33017560
- PMCID: PMC7714482
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1826619
The hippo kinase STK38 ensures functionality of XPO1
Abstract
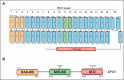
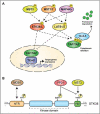
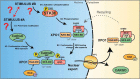
The proper segregation of basic elements such as the compartmentalization of the genome and the shuttling of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm is a crucial mechanism for homeostasis maintenance in eukaryotic cells. XPO1 (Exportin 1) is the major nuclear export receptor and is required for the export of proteins and RNAs out of the nucleus. STK38 (also known as NDR1) is a Hippo pathway serine/threonine kinase with multifarious functions in normal and cancer cells. In this review, we summarize the history of the discovery of the nucleo/cytoplasmic shuttling of proteins and focus on the major actor of nuclear export: XPO1. After describing the molecular events required for XPO1-mediated nuclear export of proteins, we introduce the Hippo pathway STK38 kinase, synthetize its regulation mechanisms as well as its biological functions in both normal and cancer cells, and finally its intersection with XPO1 biology. We discuss the recently identified mechanism of XPO1 activation by phosphorylation of XPO1_S1055 by STK38 and contextualize this finding according to the biological functions previously reported for both XPO1 and STK38, including the second identity of STK38 as an autophagy regulator. Finally, we phrase this newly identified activation mechanism into the general nuclear export machinery and examine the possible outcomes of nuclear export inhibition in cancer treatment.
Keywords: STK38; XPO1; YAP; autophagy; hippo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dobzhansky T. Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution. Am Biol Teach. 1973;35:125–129.
-
- Apple’s Jobs to Obama: ‘jobs aren’t coming back’ to U.S. - News - Sarasota Herald-Tribune, Sarasota, FL.
-
- Supply Chain 4.0 – the next-generation digital supply chain | McKinsey.
-
- CALLAN HG, RANDALL JT, TOMLIN SG.. An electron microscope study of the nuclear membrane. Nature. 1949;163:280. - PubMed
-
- Huang R, Xu Y, Wan W, et al. Deacetylation of nuclear LC3 drives autophagy initiation under starvation. Mol Cell. 2015;57:456–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases