Ultra-low-dose quadruple combination blood pressure-lowering therapy in patients with hypertension: The QUARTET randomized controlled trial protocol
- PMID: 33017580
- PMCID: PMC7531985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2020.09.017
Ultra-low-dose quadruple combination blood pressure-lowering therapy in patients with hypertension: The QUARTET randomized controlled trial protocol
Abstract
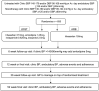
High blood pressure is the leading cause of preventable morbidity and mortality globally. Many patients remain on single-drug treatment with poor control, although guidelines recognize that most require combination therapy for blood pressure control. Our hypothesis is that a single-pill combination of 4 blood pressure-lowering agents each at a quarter dose may provide a simple, safe, and effective blood pressure-lowering solution which may also improve long-term adherence. The Quadruple UltrA-low-dose tReaTment for hypErTension (QUARTET) double-blind, active-controlled, randomized clinical trial will examine whether ultra-low-dose quadruple combination therapy is more effective than guideline-recommended standard care in lowering blood pressure. QUARTET will enroll 650 participants with high blood pressure either on no treatment or on monotherapy. Participants will be randomized 1:1 and allocated to intervention therapy of a single pill (quadpill) containing irbesartan 37.5 mg, amlodipine 1.25 mg, indapamide 0.625 mg, and bisoprolol 2.5 mg or to control therapy of a single identical-appearing pill containing irbesartan 150 mg. In both arms, step-up therapy of open-label amlodipine 5 mg will be provided if blood pressure is >140/90 at 6 weeks. The primary outcome is the difference between groups in the change from baseline in mean unattended automated office systolic blood pressure at 12-week follow-up. The primary outcome and some secondary outcomes will be assessed at 12 weeks; there is an optional 12-month extension phase to assess longer-term efficacy and tolerability. Our secondary aims are to assess if this approach is safe, has fewer adverse effects, and has better tolerability compared to standard care control. QUARTET will therefore provide evidence for the effectiveness and safety of a new paradigm in the management of high blood pressure.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
References
-
- Turnbull F. Effects of different blood-pressure-lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: results of prospectively-designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet. 2003;362:1527–1535. - PubMed
-
- Julius S., Kjeldsen S.E., Weber M. Outcomes in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk treated with regimens based on valsartan or amlodipine: the value randomised trial. Lancet. 2004;363:2022–2031. - PubMed
-
- Chow C.K., Teo K.K., Rangarajan S. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-, middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA. 2013;310:959–968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical