Zinc homeostasis and signaling in the roundworm C. elegans
- PMID: 33017595
- PMCID: PMC8237512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118882
Zinc homeostasis and signaling in the roundworm C. elegans
Abstract
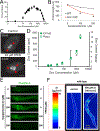
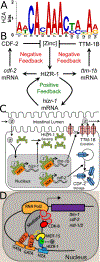
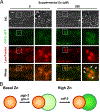
C. elegans is a powerful model for studies of zinc biology. Here we review recent discoveries and emphasize the advantages of this model organism. Methods for manipulating and measuring zinc levels have been developed in or adapted to the worm. The C. elegans genome encodes highly conserved zinc transporters, and their expression and function are beginning to be characterized. Homeostatic mechanisms have evolved to respond to high and low zinc conditions. The pathway for high zinc homeostasis has been recently elucidated based on the discovery of the master regulator of high zinc homeostasis, HIZR-1. A parallel pathway for low zinc homeostasis is beginning to emerge based on the discovery of the Low Zinc Activation promoter element. Zinc has been established to play a role in two cell fate determination events, and accumulating evidence suggests zinc may function as a second messenger signaling molecule during vulval cell development and sperm activation.
Keywords: HIZR-1; LZA; Lysosome-related organelles; Sperm activation; Vulval development; Zinc transporters.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A pathway for low zinc homeostasis that is conserved in animals and acts in parallel to the pathway for high zinc homeostasis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 16;45(20):11658-11672. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx762. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28977437 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator subunit MDT-15/MED15 and Nuclear Receptor HIZR-1/HNF4 cooperate to regulate toxic metal stress responses in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2019 Dec 9;15(12):e1008508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008508. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31815936 Free PMC article.
-
The Nuclear Receptor HIZR-1 Uses Zinc as a Ligand to Mediate Homeostasis in Response to High Zinc.PLoS Biol. 2017 Jan 17;15(1):e2000094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2000094. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Biol. 2017. PMID: 28095401 Free PMC article.
-
TGF beta-related pathways. Roles in Caenorhabditis elegans development.Trends Genet. 2000 Jan;16(1):27-33. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(99)01916-2. Trends Genet. 2000. PMID: 10637628 Review.
-
Zinc transporters as potential therapeutic targets: An updated review.J Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Feb;148(2):221-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2021.11.007. Epub 2021 Dec 2. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35063137 Review.
Cited by
-
A zinc metal complex as an NIR emissive probe for real-time dynamics and in vivo embryogenic evolution of lysosomes using super-resolution microscopy.Chem Sci. 2024 Sep 5;15(38):15659-69. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04638b. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39246364 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosome-related organelles contain an expansion compartment that mediates delivery of zinc transporters to promote homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 13;121(7):e2307143121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2307143121. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38330011 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Genetics in C. elegans Identifies Anticancer Mycotoxins Chaetocin and Chetomin as Potent Inducers of a Nuclear Metal Homeostasis Response.ACS Chem Biol. 2024 May 17;19(5):1180-1193. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00131. Epub 2024 Apr 23. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38652683 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional regulation of Chlamydomonas lysosome-related organelles during environmental changes.Plant Physiol. 2023 May 31;192(2):927-944. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad189. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36946208 Free PMC article.
-
First insight into metal binding proteins from the de novo transcriptome of acanthocephalan parasite Dentitruncus truttae.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 18;15(1):26152. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11623-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40681669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sulston JE, Schierenberg E, White JG, Thomson JN, The embryonic cell lineage of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, Dev Biol, 100 (1983) 64–119. - PubMed
-
- Sulston JE, Horvitz HR, Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, Dev Biol, 56 (1977) 110–156. - PubMed
-
- Kimble J, Hirsh D, The postembryonic cell lineages of the hermaphrodite and male gonads in Caenorhabditis elegans, Dev Biol, 70 (1979) 396–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

