Vitamin C Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Behavioral Abnormalities Triggered by Fipronil and Pyriproxyfen Insecticide Chronic Exposure on Zebrafish Juvenile
- PMID: 33019596
- PMCID: PMC7600883
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9100944
Vitamin C Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Behavioral Abnormalities Triggered by Fipronil and Pyriproxyfen Insecticide Chronic Exposure on Zebrafish Juvenile
Abstract
Chronic exposure to synthetic insecticides in the early life of a child can lead to a series of disorders. Several causes as parental age, maternal smoking, birth complications, and exposure to toxins such as insecticides on childhood can lead to Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) occurrence. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential protective role of vitamin C (Vit. C) from children's supplements after 14 days chronic exposure to insecticide mixture fipronil (Fip) + pyriproxyfen (Pyr) on juvenile zebrafish for swimming performances, social behavior and oxidative stress associated with ASD model. Juvenile (14-17 mm) wild-type AB zebrafish (Danio rerio) (45 days) were exposed to relevant concentrations: vit. C (25 µg L-1), Fip (600 µg L-1/1.372 μM) + Pyr (600 µg L-1/1.89 μM), and [Fip (600 µg L-1/1.372 μM) + Pyr (600 µg L-1 /1.89 μM)] + vit. C (25 µg L-1). Our results showed that insecticides can disturb the social behavior of zebrafish during 14 days of the administration, decreased the swimming performances, and elevated the oxidative stress biomarkers of SOD (superoxide dismutase), GPx (glutathione peroxidase), and MDA (malondialdehyde). The vitamin C supplement significantly attenuated the neurotoxicity of insecticide mixture and oxidative stress. This study provides possible in vivo evidence to show that vitamin C supplements could attenuate oxidative stress and brain damage of fipronil and pyriproxyfen insecticide chronic exposure on zebrafish juvenile.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; insecticides; neurotoxicity; protective role; social behavior; vitamin C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
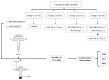


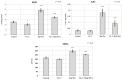
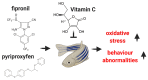
References
-
- Gupta R.C., Milatovic D. Biomarkers in Toxicology. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2019. Insecticides.1222p
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

