Beta Cell Imaging-From Pre-Clinical Validation to First in Man Testing
- PMID: 33019671
- PMCID: PMC7582644
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21197274
Beta Cell Imaging-From Pre-Clinical Validation to First in Man Testing
Abstract
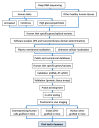
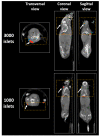
There are presently no reliable ways to quantify human pancreatic beta cell mass (BCM) in vivo, which prevents an accurate understanding of the progressive beta cell loss in diabetes or following islet transplantation. Furthermore, the lack of beta cell imaging hampers the evaluation of the impact of new drugs aiming to prevent beta cell loss or to restore BCM in diabetes. We presently discuss the potential value of BCM determination as a cornerstone for individualized therapies in diabetes, describe the presently available probes for human BCM evaluation, and discuss our approach for the discovery of novel beta cell biomarkers, based on the determination of specific splice variants present in human beta cells. This has already led to the identification of DPP6 and FXYD2ga as two promising targets for human BCM imaging, and is followed by a discussion of potential safety issues, the role for radiochemistry in the improvement of BCM imaging, and concludes with an overview of the different steps from pre-clinical validation to a first-in-man trial for novel tracers.
Keywords: MRI; PET; SPECT; beta cell imaging; pancreas; pre-clinical validation; radiochemistry; type 1 diabetes; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
D.L.E. has patents for the use of FXYD2γα and DPP6 and the tracers targeting them for pancreatic islet cell imaging.
Figures

References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. [(accessed on 25 January 2020)]; Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

