LncLocation: Efficient Subcellular Location Prediction of Long Non-Coding RNA-Based Multi-Source Heterogeneous Feature Fusion
- PMID: 33019721
- PMCID: PMC7582431
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21197271
LncLocation: Efficient Subcellular Location Prediction of Long Non-Coding RNA-Based Multi-Source Heterogeneous Feature Fusion
Abstract
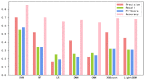
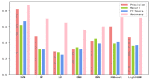
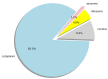
Recent studies uncover that subcellular location of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) can provide significant information on its function. Due to the lack of experimental data, the number of lncRNAs is very limited, experimentally verified subcellular localization, and the numbers of lncRNAs located in different organelle are wildly imbalanced. The prediction of subcellular location of lncRNAs is actually a multi-classification small sample imbalance problem. The imbalance of data results in the poor recognition effect of machine learning models on small data subsets, which is a puzzling and challenging problem in the existing research. In this study, we integrate multi-source features to construct a sequence-based computational tool, lncLocation, to predict the subcellular location of lncRNAs. Autoencoder is used to enhance part of the features, and the binomial distribution-based filtering method and recursive feature elimination (RFE) are used to filter some of the features. It improves the representation ability of data and reduces the problem of unbalanced multi-classification data. By comprehensive experiments on different feature combinations and machine learning models, we select the optimal features and classifier model scheme to construct a subcellular location prediction tool, lncLocation. LncLocation can obtain an 87.78% accuracy using 5-fold cross validation on the benchmark data, which is higher than the state-of-the-art tools, and the classification performance, especially for small class sets, is improved significantly.
Keywords: logarithm-distance of Hexamer; multi-source features; subcellullar location; the binomial distribution-based filtering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MVSLLnc: LncRNA subcellular localization prediction based on multi-source features and two-stage voting strategy.Methods. 2025 Feb;234:324-332. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2025.01.013. Epub 2025 Jan 19. Methods. 2025. PMID: 39837434
-
SubLocEP: a novel ensemble predictor of subcellular localization of eukaryotic mRNA based on machine learning.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbaa401. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa401. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33388743
-
Locate-R: Subcellular localization of long non-coding RNAs using nucleotide compositions.Genomics. 2020 May;112(3):2583-2589. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.02.011. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32068122
-
Pattern recognition analysis on long noncoding RNAs: a tool for prediction in plants.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Mar 25;20(2):682-689. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby034. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29697740 Review.
-
Global Positioning System: Understanding Long Noncoding RNAs through Subcellular Localization.Mol Cell. 2019 Mar 7;73(5):869-883. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.008. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30849394 Review.
Cited by
-
An ensemble deep learning framework for multi-class LncRNA subcellular localization with innovative encoding strategy.BMC Biol. 2025 Feb 21;23(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02148-4. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 39984880 Free PMC article.
-
RNALoc-LM: RNA subcellular localization prediction using pre-trained RNA language model.Bioinformatics. 2025 Mar 29;41(4):btaf127. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf127. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40119908 Free PMC article.
-
EL-RMLocNet: An explainable LSTM network for RNA-associated multi-compartment localization prediction.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jul 26;20:3986-4002. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.07.031. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35983235 Free PMC article.
-
LncLocFormer: a Transformer-based deep learning model for multi-label lncRNA subcellular localization prediction by using localization-specific attention mechanism.Bioinformatics. 2023 Dec 1;39(12):btad752. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad752. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 38109668 Free PMC article.
-
MSLP: mRNA subcellular localization predictor based on machine learning techniques.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Mar 22;24(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05232-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36949389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fitzpatrick C., Bendek M.F., Briones M., Farfan N., Silva V.A., Nardocci G., Montecino M., Boland A., Deleuze J.F., Villegas J., et al. Mitochondrial ncRNA targeting induces cell cycle arrest and tumor growth inhibition of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through reduction of key cell cycle progression factors. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:423. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1649-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

