Olorofim Susceptibility Testing of 1,423 Danish Mold Isolates Obtained in 2018-2019 Confirms Uniform and Broad-Spectrum Activity
- PMID: 33020160
- PMCID: PMC7927864
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01527-20
Olorofim Susceptibility Testing of 1,423 Danish Mold Isolates Obtained in 2018-2019 Confirms Uniform and Broad-Spectrum Activity
Abstract
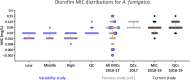
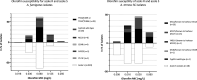
Olorofim is a novel antifungal drug in phase 2 trials. It has shown promising in vitro activity against various molds, except for Mucorales. Initially, we observed a broad range of EUCAST MICs for Aspergillus fumigatus Here, we explored the MIC variability in more detail and prospectively investigated the susceptibility of contemporary clinical mold isolates, as population data are needed for future epidemiological cutoff (ECOFF) settings. Fifteen A. fumigatus isolates previously found with low/medium/high MICs (≤0.002 to 0.25 mg/liter) were tested repeatedly and EUCAST MICs read in a blinded fashion by three observers. pyrE, encoding the olorofim target enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), was sequenced. A total of 1,423 mold isolates (10 Aspergillus species complexes [including 1,032 A. fumigatus isolates] and 105 other mold/dermatophyte isolates) were examined. Olorofim susceptibility (modal MIC, MIC50, MIC90, and wild-type upper limits [WT-ULs] [species complexes with ≥15 isolates]) was determined and compared to that of four comparators. MICs (mg/liter) were within two 2-fold dilutions (0.016 to 0.03) for 473/476 determinations. The MIC range spanned four dilutions (0.008 to 0.06). No significant pyrE mutations were found. Modal MIC/WT-UL97.5 (mg/liter) values were 0.03/0.06 (A. terreus and A. flavus), 0.06/0.125 (A. fumigatus and Trichophyton rubrum), and 0.06/0.25 (A. niger and A. nidulans). The MIC range for Scedosporium spp. was 0.008 to 0.25. Olorofim susceptibility was similar for azole-resistant and -susceptible isolates of A. fumigatus but reduced for A. montevidensis and A. chevalieri (MICs of >1). With experience, olorofim susceptibility testing is robust. The testing of isolates from our center showed uniform and broad-spectrum activity. Single-center WT-ULs are suggested.
Keywords: Aspergillus; Cyp51A; DHODH; EUCAST; F901318; Scedosporium; antifungal susceptibility; azole resistance; olorofim; pyrE.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EUCAST olorofim MICs for 3,550 Danish mold and dermatophyte isolates from 2020 to 2023.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Aug 6;69(8):e0035325. doi: 10.1128/aac.00353-25. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40569754 Free PMC article.
-
EUCAST Determination of Olorofim (F901318) Susceptibility of Mold Species, Method Validation, and MICs.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Jul 27;62(8):e00487-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00487-18. Print 2018 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29784842 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of the novel antifungal compound F901318 against difficult-to-treat Aspergillus isolates.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 Sep 1;72(9):2548-2552. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx177. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28605488
-
Review of the novel antifungal drug olorofim (F901318).BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Nov 7;24(1):1256. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10143-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39511507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isavuconazole: A new broad-spectrum azole. Part 1: In vitro activity.J Mycol Med. 2018 Mar;28(1):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Mar 11. J Mycol Med. 2018. PMID: 29534853 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical outcomes of intensive care unit patients infected with multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria treated with ceftazidime/avibactam and ceftolozane/tazobactam.Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Mar;55(1):333-341. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-01193-x. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38133795 Free PMC article.
-
Trends of Azole-Resistant Aspergillus Fumigatus Susceptibility Over 12 Years from a German ECMM Excellence Center.Mycopathologia. 2025 Apr 5;190(2):34. doi: 10.1007/s11046-025-00941-x. Mycopathologia. 2025. PMID: 40186715 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus strains that evolve resistance to the agrochemical fungicide ipflufenoquin in vitro are also resistant to olorofim.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Jan;9(1):29-34. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01542-4. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38151646 Free PMC article.
-
The Antifungal Pipeline: Fosmanogepix, Ibrexafungerp, Olorofim, Opelconazole, and Rezafungin.Drugs. 2021 Oct;81(15):1703-1729. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01611-0. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34626339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel antifungals and treatment approaches to tackle resistance and improve outcomes of invasive fungal disease.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Jun 13;37(2):e0007423. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00074-23. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38602408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lackner M, Birch M, Naschberger V, Grässle D, Beckmann N, Warn P, Gould J, Law D, Lass-Flörl C, Binder U. 2018. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor olorofim exhibits promising activity against all clinically relevant species within Aspergillus section Terrei. J Antimicrob Chemother 73:3068–3073. doi:10.1093/jac/dky329. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oliver JD, Sibley GEMM, Beckmann N, Dobb KS, Slater MJ, McEntee L, Du Pré S, Livermore J, Bromley MJ, Wiederhold NP, Hope WW, Kennedy AJ, Law D, Birch M. 2016. F901318 represents a novel class of antifungal drug that inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:12809–12814. doi:10.1073/pnas.1608304113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

