Angiostatic cues from the matrix: Endothelial cell autophagy meets hyaluronan biology
- PMID: 33020183
- PMCID: PMC7864073
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.014391
Angiostatic cues from the matrix: Endothelial cell autophagy meets hyaluronan biology
Abstract
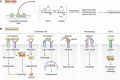
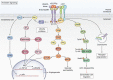
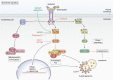
The extracellular matrix encompasses a reservoir of bioactive macromolecules that modulates a cornucopia of biological functions. A prominent body of work posits matrix constituents as master regulators of autophagy and angiogenesis and provides molecular insight into how these two processes are coordinated. Here, we review current understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying hyaluronan and HAS2 regulation and the role of soluble proteoglycan in affecting autophagy and angiogenesis. Specifically, we assess the role of proteoglycan-evoked autophagy in regulating angiogenesis via the HAS2-hyaluronan axis and ATG9A, a novel HAS2 binding partner. We discuss extracellular hyaluronan biology and the post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications that regulate its main synthesizer, HAS2. We highlight the emerging group of proteoglycans that utilize outside-in signaling to modulate autophagy and angiogenesis in cancer microenvironments and thoroughly review the most up-to-date understanding of endorepellin signaling in vascular endothelia, providing insight into the temporal complexities involved.
Keywords: AMP-activated kinase (AMPK); angiogenesis; autophagy; cell signaling; decorin; endothelial cell; extracellular matrix; hyaluronan; hyaluronan synthase 2; perlecan; proteoglycan; vascular biology.
© 2020 Chen and Iozzo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Cohen I.R., Murdoch A.D., Naso M.F., Marchetti D., Berd D., Iozzo R.V. Abnormal expression of perlecan proteoglycan in metastatic melanomas. Cancer Res. 1994;54:5771–5774. 7954396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

