Immune checkpoint inhibitor associated reactivation of primary membranous nephropathy responsive to rituximab
- PMID: 33020246
- PMCID: PMC7537330
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001287
Immune checkpoint inhibitor associated reactivation of primary membranous nephropathy responsive to rituximab
Abstract
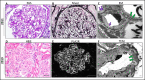
The same mechanisms that mediate antitumor immunity from checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) can also lead to unintended targeting of normal tissues, characterized as immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Those with pre-existing autoimmune disease are believed to be particularly vulnerable for exacerbating underlying autoimmunity or inducing severe irAEs. We report the first case of CPI-associated reactivation of primary membranous nephropathy (MN) in a patient with pleural mesothelioma responding to immunotherapy. Due to its specificity in targeting B-lymphocytes, rituximab was used to treat primary MN with the expectation that this would not interfere with the benefits gained from T cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Rituximab was effective in treating CPI-associated reactivation of MN, and the patient was successfully rechallenged with nivolumab and maintained stable kidney function and sustained clinical antitumor effect. While exacerbation of pre-existing autoimmune diseases from CPIs is common, therapy for autoimmune reactivation can be rationally directed by an understanding of the immunosuppressive mechanism with goals of cancer treatment.
Keywords: autoimmunity; case reports; immunotherapy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Lefaucheur C, Stengel B, Nochy D, et al. . Membranous nephropathy and cancer: epidemiologic evidence and determinants of high-risk cancer association. Kidney Int 2006;70:1510–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
