Exogenous Abscisic Acid Can Influence Photosynthetic Processes in Peas through a Decrease in Activity of H+-ATP-ase in the Plasma Membrane
- PMID: 33020382
- PMCID: PMC7650568
- DOI: 10.3390/biology9100324
Exogenous Abscisic Acid Can Influence Photosynthetic Processes in Peas through a Decrease in Activity of H+-ATP-ase in the Plasma Membrane
Abstract
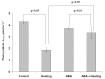
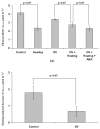
Abscisic acid (ABA) is an important hormone in plants that participates in their acclimation to the action of stressors. Treatment by exogenous ABA and its synthetic analogs are a potential way of controlling the tolerance of agricultural plants; however, the mechanisms of influence of the ABA treatment on photosynthetic processes require further investigations. The aim of our work was to investigate the participation of inactivation of the plasma membrane H+-ATP-ase on the influence of ABA treatment on photosynthetic processes and their regulation by electrical signals in peas. The ABA treatment of seedlings was performed by spraying them with aqueous solutions (10-5 M). The combination of a Dual-PAM-100 PAM fluorometer and GFS-3000 infrared gas analyzer was used for photosynthetic measurements; the patch clamp system on the basis of a SliceScope Pro 2000 microscope was used for measurements of electrical activity. It was shown that the ABA treatment stimulated the cyclic electron flow around photosystem I and decreased the photosynthetic CO2 assimilation, the amplitude of burning-induced electrical signals (variation potentials), and the magnitude of photosynthetic responses relating to these signals; in contrast, treatment with exogenous ABA increased the heat tolerance of photosynthesis. An investigation of the influence of ABA treatment on the metabolic component of the resting potential showed that this treatment decreased the activity of the H+-ATP-ase in the plasma membrane. Inhibitor analysis using sodium orthovanadate demonstrated that this decrease may be a mechanism of the ABA treatment-induced changes in photosynthetic processes, their heat tolerance, and regulation by electrical signals.
Keywords: CO2 assimilation; H+-ATP-ase; abscisic acid (ABA); electrical signals; photosynthesis; photosynthetic heat tolerance; photosynthetic regulation; variation potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Inactivation of H+-ATPase Participates in the Influence of Variation Potential on Photosynthesis and Respiration in Peas.Plants (Basel). 2020 Nov 16;9(11):1585. doi: 10.3390/plants9111585. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33207655 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Burning-Induced Electrical Signals on Photosynthesis in Pea Can Be Modified by Soil Water Shortage.Plants (Basel). 2022 Feb 17;11(4):534. doi: 10.3390/plants11040534. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214867 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Treatment by Exogenous 24-Epibrassinolide Influences Burning-Induced Electrical Signals and Following Photosynthetic Responses in Pea (Pisum sativum L.).Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 23;13(23):3292. doi: 10.3390/plants13233292. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39683085 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical signals as mechanism of photosynthesis regulation in plants.Photosynth Res. 2016 Dec;130(1-3):373-387. doi: 10.1007/s11120-016-0270-x. Epub 2016 May 6. Photosynth Res. 2016. PMID: 27154573 Review.
-
Electrical Signals, Plant Tolerance to Actions of Stressors, and Programmed Cell Death: Is Interaction Possible?Plants (Basel). 2021 Aug 19;10(8):1704. doi: 10.3390/plants10081704. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ratio of Intensities of Blue and Red Light at Cultivation Influences Photosynthetic Light Reactions, Respiration, Growth, and Reflectance Indices in Lettuce.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jan 1;11(1):60. doi: 10.3390/biology11010060. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053058 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Photochemical Reflectance Indices as New Tool for Revealing Influence of Drought and Heat on Pea and Wheat Plants.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 14;11(10):1308. doi: 10.3390/plants11101308. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631733 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokinin and abscisic acid alleviate drought stress through changing organic acids profile, ion immolation, and fatty acid profile to improve yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022 May;28(5):1119-1129. doi: 10.1007/s12298-022-01173-9. Epub 2022 May 24. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022. PMID: 35722511 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ABA Pre-Treatment on Rice Plant Transcriptome Response to Multiple Abiotic Stress.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 20;13(10):1554. doi: 10.3390/biom13101554. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892236 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Modified Farquhar-von Caemmerer-Berry Model Describing Photodamage of Photosynthetic Electron Transport in C3 Plants under Different Temperatures.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 8;12(18):3211. doi: 10.3390/plants12183211. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765375 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

