Neuroprotective Effects of Chronic Resveratrol Treatment and Exercise Training in the 3xTg-AD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33020412
- PMCID: PMC7582460
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21197337
Neuroprotective Effects of Chronic Resveratrol Treatment and Exercise Training in the 3xTg-AD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
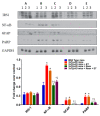
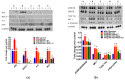
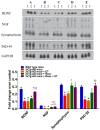
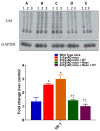
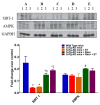
To date, there is no cure or effective treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD), a chronic neurodegenerative condition that affects memory, language, and behavior. AD is characterized by neuroinflammation, accumulation of brain amyloid-beta (Aβ) oligomers and neurofibrillary tangles, increased neuronal apoptosis, and loss of synaptic function. Promoting regular exercise and a diet containing polyphenols are effective non-pharmacological approaches that prevent the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. In this study, we measured various conformational toxic species of Aβ and markers of inflammation, apoptosis, endolysosomal degradation, and neuroprotection after 5 months of exercise training (ET), resveratrol (Resv) treatment, or combination treatment in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of AD. Our main results indicate that Resv decreased neuroinflammation and accumulation of Aβ oligomers, increased levels of neurotrophins, synaptic markers, silent information regulator, and decreased markers of apoptosis, autophagy, endolysosomal degradation and ubiquitination in the brains of 3xTg-AD mice. ET improved some markers related to neuroprotection, but when combined with Resv treatment, the benefits achieved were as effective as Resv treatment alone. Our results show that the neuroprotective effects of Resv, ET or Resv and ET are associated with reduced toxicity of Aβ oligomers, suppression of neuronal autophagy, decreased apoptosis, and upregulation of key growth-related proteins.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-beta; apoptosis; autophagy; brain; exercise; neuroinflammation; neurotrophin; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Beneficial effects of resveratrol and exercise training on cardiac and aortic function and structure in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Apr 17;13:1197-1211. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S196119. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31114160 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Induces Brain Resilience Against Alzheimer Neurodegeneration Through Proteostasis Enhancement.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Feb;56(2):1502-1516. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1157-y. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29948950
-
The Beneficial Effects of Combined Exercise and Polyphenols in Alzheimer's Disease.Phytother Res. 2025 Feb;39(2):1020-1034. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8422. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Phytother Res. 2025. PMID: 39716920 Review.
-
Artemether Activation of AMPK/GSK3β(ser9)/Nrf2 Signaling Confers Neuroprotection towards β-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity in 3xTg Alzheimer's Mouse Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 21;2019:1862437. doi: 10.1155/2019/1862437. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31871541 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol and neuroprotection: an insight into prospective therapeutic approaches against Alzheimer's disease from bench to bedside.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jul;59(7):4384-4404. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02859-7. Epub 2022 May 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35545730 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut Microbiota and its Metabolites: Bridge of Dietary Nutrients and Alzheimer's Disease.Adv Nutr. 2023 Jul;14(4):819-839. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Adv Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37075947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-Based Bioactive Molecules in Improving Health and Preventing Lifestyle Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 15;22(6):2991. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062991. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804225 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic exercise combined with chlorogenic acid exerts neuroprotective effects and reverses cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease model mice (APP/PS1) via the SIRT1/ /PGC-1α/PPARγ signaling pathway.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 16;15:1269952. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1269952. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38046466 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 Is Involved in the Neuroprotection of Pterostilbene Against Amyloid β 25-35-Induced Cognitive Deficits in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 14;13:877098. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.877098. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35496289 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Regulation of Gut-Brain Axis in Alzheimer's Disease: Importance of Microbiota Metabolites.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 19;15:736814. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.736814. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Alzheimer Report 2018. [(accessed on 18 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/world-report-2018.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

