The Biomarker and Therapeutic Potential of Circular Rnas in Schizophrenia
- PMID: 33020462
- PMCID: PMC7601372
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9102238
The Biomarker and Therapeutic Potential of Circular Rnas in Schizophrenia
Abstract
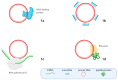
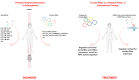
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are endogenous, single-stranded, most frequently non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecules that play a significant role in gene expression regulation. Circular RNAs can affect microRNA functionality, interact with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), translate proteins by themselves, and directly or indirectly modulate gene expression during different cellular processes. The affected expression of circRNAs, as well as their targets, can trigger a cascade of events in the genetic regulatory network causing pathological conditions. Recent studies have shown that altered circular RNA expression patterns could be used as biomarkers in psychiatric diseases, including schizophrenia (SZ); moreover, circular RNAs together with other cell molecules could provide new insight into mechanisms of this disorder. In this review, we focus on the role of circular RNAs in the pathogenesis of SZ and analyze their biomarker and therapeutic potential in this disorder.
Keywords: RBPs; biomarkers; circRNAs; circular RNAs; expression; microRNAs; schizophrenia; sponge; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emergent Roles of Circular RNAs in Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 18;23(3):1032. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031032. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35162956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The alterations of circular RNA expression in plasma exosomes from patients with schizophrenia.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Jan;236(1):458-467. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29873. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32542700
-
Circular RNAs: Regulatory functions in respiratory tract cancers.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Nov;510:264-271. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.07.042. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32710944 Review.
-
CircRNAs: A new perspective of biomarkers in the nervous system.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Aug;128:110251. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110251. Epub 2020 May 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32480219 Review.
-
Identification of atrial fibrillation-related circular RNAs and constructing the integrative regulatory network of circular RNAs, microRNAs and mRNAs by bioinformatics analysis.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020 Oct 31;66(7):161-168. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020. PMID: 33287936
Cited by
-
CircPrime: a web-based platform for design of specific circular RNA primers.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 May 19;24(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05331-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37208611 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives in CNS Diseases.Curr Med Sci. 2023 Oct;43(5):879-889. doi: 10.1007/s11596-023-2784-8. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Curr Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37815742 Review.
-
Circular RNAs: Non-Canonical Observations on Non-Canonical RNAs.Cells. 2023 Jan 14;12(2):323. doi: 10.3390/cells12020323. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lightbody G., Haberland V., Browne F., Taggart L., Zheng H., Parkes E., Blayney J.K. Review of applications of high-throughput sequencing in personalized medicine: Barriers and facilitators of future progress in research and clinical application. Brief. Bioinform. 2019;20:1795–1811. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ershova E.S., Jestkova E.M., Martynov A.V., Shmarina G.V., Umriukhin P.E., Bravve L.V., Zakharova N.V., Kostyuk G.P., Saveliev D.V., Orlova M.D., et al. Accumulation of Circulating Cell-Free CpG-Enriched Ribosomal DNA Fragments on the Background of High Endonuclease Activity of Blood Plasma in Schizophrenic Patients. Int. J. Genomics. 2019;2019:8390585. doi: 10.1155/2019/8390585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

