Distinct signatures of gut microbiome and metabolites associated with significant fibrosis in non-obese NAFLD
- PMID: 33020474
- PMCID: PMC7536225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18754-5
Distinct signatures of gut microbiome and metabolites associated with significant fibrosis in non-obese NAFLD
Abstract
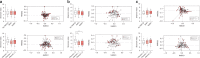
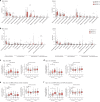
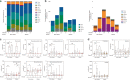
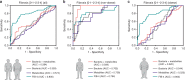
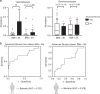
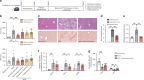
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with obesity but also found in non-obese individuals. Gut microbiome profiles of 171 Asians with biopsy-proven NAFLD and 31 non-NAFLD controls are analyzed using 16S rRNA sequencing; an independent Western cohort is used for external validation. Subjects are classified into three subgroups according to histological spectra of NAFLD or fibrosis severity. Significant alterations in microbiome diversity are observed according to fibrosis severity in non-obese, but not obese, subjects. Ruminococcaceae and Veillonellaceae are the main microbiota associated with fibrosis severity in non-obese subjects. Furthermore, stool bile acids and propionate are elevated, especially in non-obese subjects with significant fibrosis. Fibrosis-related Ruminococcaceae and Veillonellaceae species undergo metagenome sequencing, and four representative species are administered in three mouse NAFLD models to evaluate their effects on liver damage. This study provides the evidence for the role of the microbiome in the liver fibrosis pathogenesis, especially in non-obese subjects.
Conflict of interest statement
G.P.K. is a founder of KoBioLabs, Inc., a company characterizing the role of host–microbiome interaction in chronic diseases. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Chalasani N, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1592–1609. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

