Impact of Heat Index and Ultraviolet Index on COVID-19 in Major Cities of Pakistan
- PMID: 33021515
- PMCID: PMC7864608
- DOI: 10.1097/JOM.0000000000002039
Impact of Heat Index and Ultraviolet Index on COVID-19 in Major Cities of Pakistan
Abstract
Introduction: The world population is under the grip of global pandemic of COVID-19. The present study analyzed relationship between meteorological parameters and COVID-19 in three major cities of Pakistan, that is, Karachi, Lahore, and Peshawar.
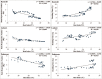
Methods: The impacts of heat index (HI) and ultraviolet index (UVI) over daily COVID-19 cases have examined to identify its transmission and propagation. The significance of basic reproductive number (R0), growth rate (Gr) and doubling time (Td) of COVID-19 with HI and UVI was determined.
Results: Both indices show a significant positive correlation (at 5% significance level) to R0, Td, and Gr of COVID-19 patients. Our results showed that the minimum threshold temperature of 33 °C for HI (with a positive variation of 3 °C to 5 °C) put a significant impact on new cases.
Conclusion: HI and UVI impacted significantly to decline COVID-19 cases over the region.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Paz S, Semenza JC. El Niño and climate change—contributing factors in the dispersal of Zika virus in the Americas? Lancet 2016; 387:745. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Chowell G. Exploring optimal control strategies in seasonally varying flu-like epidemics. J Theor Biol 2017; 412:36–47. - PubMed
-
- Morin CW, Stoner-Duncan B, Winker K, et al. Avian influenza virus ecology and evolution through a climatic lens. Environ Int 2018; 119:241–249. - PubMed
-
- Keilman LJ. Seasonal influenza (flu). Nurs Clin 2019; 54:227–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

