Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes 2019
- PMID: 33021749
- PMCID: PMC7378414
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13306
Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes 2019
Keywords: Diabetes; Diagnosis; Guideline; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Eiichi Araki received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Kowa, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Novo Nordisk, Ono Pharmaceutical and Sanofi, also received subsidies or donations from Astellas Pharma, Bayer Yakuhin, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly Japan, Kowa, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer Japan, Sanofi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Taisho Pharmaceutical and Takeda Pharmaceutical, and belongs to endowed departments by MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical and Terumo. Mitsuhiko Noda received subsidies or donations from Astellas Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly Japan, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Ono Pharmaceutical, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical and Teijin Pharma. Hiroshi Noto received honoraria from Eli Lilly Japan and MSD. Haruhiko Osawa received research funding from Daiichi Sankyo, Ono Pharmaceutical, Sysmex, Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical and Takeda Pharmaceutical. Yukio Tanizawa received honoraria from Astellas Pharma, MSD, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Ono Pharmaceutical and Takeda Pharmaceutical, also received research funding from Seastar, also received subsidies or donations from Astellas Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly Japan, Kyowa Kirin, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, MSD, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma and Takeda Pharmaceutical. Kazuyuki Tobe received honoraria from Novo Nordisk Pharma, Kowa Pharmaceutical and Astellas Pharma, also received research funding from The Uehara Memorial Foundation and The Naito Foundation, also received subsidies or donations from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, Asahi Kasei Pharma, Teijin Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ono Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Eli Lilly Japan, Fuji Chemical Industries and Arkray. Narihito Yoshioka received honoraria from Novo Nordisk Pharma and Takeda Pharmaceutical. Atsushi Goto, Tatsuya Kondo, Hideki Origasa, Akihiko Taguchi have nothing to declare.
Figures


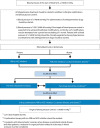

References
-
- Kosaka K, Akanuma Y, Goto Y, et al Report of Committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Jpn Diabetes Soc 1982; 25: 859–866 (Japanese).
-
- World Health Organization . Report of a WHO Consultation: Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes MELLITUS and its Complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization Department of Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance, 1999. Available from: http://www.staff.ncl.ac.uk/philip.home/who_dmc.htm.
-
- Kuzuya T, Nakagawa S, Satoh J, et al Report of the Committee of Japan Diabetes Society on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Jpn Diabetes Soc 1999; 42: 385–404 (Japanese).
-
- American Diabetes Association . Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 2018; 41(Suppl 1): S13–S27. - PubMed
2 GOALS AND STRATEGIES FOR DIABETES MANAGEMENT
-
- United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group . Intensive blood‐glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998; 352: 837–853. - PubMed
-
- Look ARG, Gregg EW, Jakicic JM, et al Association of the magnitude of weight loss and changes in physical fitness with long‐term cardiovascular disease outcomes in overweight or obese people with type 2 diabetes: a post‐hoc analysis of the Look AHEAD randomised clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2016; 4: 913–921. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sone H, Tanaka S, Tanaka S, et al Serum level of triglycerides is a potent risk factor comparable to LDL cholesterol for coronary heart disease in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: subanalysis of the Japan Diabetes Complications Study (JDCS). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 96: 3448–3456. - PubMed
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, et al Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J‐DOIT3): an open‐label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017; 5: 951–964. - PubMed
3 MEDICAL NUTRITION THERAPY (MNT)
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, et al Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 1343–1350 [level 1]. - PubMed
-
- Terranova CO, Brakenridge CL, Lawler SP, et al Effectiveness of lifestyle‐based weight loss interventions for adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015; 17: 371–378 [level 1]. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Pei JH, Kuang J, et al Effect of lifestyle intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta‐analysis. Metabolism 2015; 64: 338–347 [level 1]. - PubMed
4 PHYSICAL ACTIVITY/EXERCISE
-
- Umpierre D, Ribeiro PA, Kramer CK, et al Physical activity advice only or structured exercise training and association with HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. JAMA 2011; 305: 1790–1799 [level 1+]. - PubMed
-
- Boulé NG, Haddad E, Kenny GP, et al Effects of exercise on glycemic control and body mass in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta‐analysis of controlled clinical trials. JAMA 2001; 286: 1218–1227 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Pai LW, Li TC, Hwu YJ, et al The effectiveness of regular leisure‐time physical activities on long‐term glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2016; 113: 77–85 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Boniol M, Dragomir M, Autier P, et al Physical activity and change in fasting glucose and HbA1c: a quantitative meta‐analysis of randomized trials. Acta Diabetol 2017; 54: 983–991 [level 1+]. - PubMed
-
- MacLeod SF, Terada T, Chahal BS, et al Exercise lowers postprandial glucose but not fasting glucose in type 2 diabetes: a meta‐analysis of studies using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2013; 29: 593–603 [level 2]. - PubMed
5 TREATMENT WITH GLUCOSE‐LOWERING AGENTS (EXCLUDING INSULIN)
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group . Intensive blood‐glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998; 352: 837–853. - PubMed
-
- Bennett WL, Wilson LM, Bolen S, et al Oral diabetes medications for adults with type 2 diabetes: an update. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), 2011. - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group . Effect of intensive blood‐glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998; 352: 854–865. - PubMed
6 INSULIN THERAPY
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) Research Group . Early worsening of diabetic retinopathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Arch Ophthalmol 1998; 116: 874–886. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi Y, Takayama S, Ito T, et al Clinical features of eighty‐six diabetic patients with post‐treatment painful neuropathy. J Jpn Diabetes Soc 1998; 41: 165–170 (Japanese).
-
- United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group . United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study 24: a 6‐year, randomized, controlled trial comparing sulfonylurea, insulin, and metformin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes that could not be controlled with diet therapy. Ann Intern Med 1998; 128: 165–175. - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) Research Group . The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long‐term complications in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 977–986 [level 1]. - PubMed
7 DIABETES SELF‐MANAGEMENT EDUCATION AND SUPPORT FOR THE SELF‑MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES
-
- He X, Li J, Wang B, et al Diabetes self‐management education reduces risk of all‐cause mortality in type 2 diabetes patients: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Endocrine 2017; 55: 712–731 [level 1+]. - PubMed
-
- Ismail K, Winkley K, Rabe‐Hesketh S. Systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials of psychological interventions to improve glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2004; 363, 1589–1597 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Pillay J, Armstrong MJ, Butalia S, et al Behavioral programs for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163: 848–860 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Pillay J, Armstrong MJ, Butalia S, et al Behavioral programs for type 1 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163: 836–847 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Rickheim PL, Weaver TW, Flader JL, et al Assessment of group versus individual diabetes education: a randomized study. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 269–274 [level 1]. - PubMed
8 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, et al The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: IX. Four‐year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. Arch Ophthalmol 1989; 107: 237–243 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, et al Ⅹ. Four‐year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is 30 years or more. Arch Ophthalmol 1989; 107: 244–249 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Younis N, Broadbent DM, Vora JP, et al Incidence of sight‐threatening retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes in the Liverpool Diabetic Eye Study: a cohort study. Lancet 2003; 361: 195–200 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Misra A, Bachmann MO, Greenwood RH, et al Trends in yield and effects of screening intervals during 17 years of a large UK community‐based diabetic retinopathy screening programme. Diabet Med 2009; 26: 1040–1047 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group . The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long‐term complications in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 977–986 [level 1]. - PubMed
9 DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY
-
- Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, et al Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis 2009; 53: 982–992. - PubMed
-
- Horio M, Imai E, Yasuda Y, et al GFR estimation using standardized serum cystatin C in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis 2013; 61: 197–203. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes C , Complications Trial Research Group , Nathan DM, et al The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long‐term complications in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 977–986 [level 1]. - PubMed
10 DIABETIC NEUROPATHY
-
- Hotta N, Toyoda R. Diabetic Neuropathy. Kanehara, Tokyo, 1996. p. 145–154 (Japanese).
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, et al Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 956–962. - PubMed
-
- Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton SE, et al Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 341–350. - PubMed
11 DIABETIC FOOT
-
- IWGDF Guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease. https://iwgdfguidelines.org/wp‐content/uploads/2019/05/IWGDF‐Guidelines‐....
-
- Frykberg RG, Zgonis T, Armstrong DG, et al Diabetic foot disorders: a clinical practice guideline (2006 revision). J Foot Ankle Surg 2006; 45: S1–S66. - PubMed
-
- Krishinan S, Nash F, Baker N et al Reduction in diabetic amputations over 11 years in a defined U.K. population benefits of multidisciplinary team work and continuous prospective audit. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: 99–101 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Malone JM, Snyder M, Anderson G, et al Prevention of amputation by diabetic education. Am J Surg 1989; 158: 520–524 [level 1]. - PubMed
12 DIABETIC MACROANGIOPATHY
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, et al Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 383–393. - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Lund‐Andersen H, Parving HH, et al Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 580–591. - PubMed
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, et al Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J‐DOIT3): an open‐label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017; 5: 951–964. - PubMed
13 DIABETES AND PERIODONTITIS
-
- Takahashi K, Nishimura F, Kurihara M, et al Subgingival microflora and antibody responses against periodontal bacteria of young Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Int Acad Periodontol 2001; 3: 104–111. - PubMed
-
- Morita I, Inagaki K, Nakamura F, et al Relationship between periodontal status and levels of glycated hemoglobin. J Dent Res 2012; 91: 161–166. - PubMed
-
- Graziani F, Gennai S, Solini A, et al A systematic review and meta‐analysis of epidemiologic observational evidence on the effect of periodontitis on diabetes An update of the EFP‐AAP review. J Clin Periodontol 2018; 45: 167–187. - PubMed
14 DIABETES COMPLICATED BY OBESITY (INCLUDING METABOLIC SYNDROME)
-
- Matsuzawa Y, Sakata T, Ikeda Y, et al Guidelines for the management of obesity disease 2006. 2006: 1–91 (Japanese).
-
- Examination Committee of Criteria for ‘Obesity Disease’ in Japan , Japan Society for the Study of Obesity . New criteria for ‘obesity disease’ in Japan. Circ J 2002; 66: 987–992. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T, Boyko EJ, McNeely MJ, et al Minimum waist and visceral fat values for identifying Japanese Americans at risk for the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 120–127. - PubMed
-
- Kashihara H, Lee JS, Kawakubo K, et al Criteria of waist circumference according to computed tomography‐measured visceral fat area and the clustering of cardiovascular risk factors. Circ J 2009; 73: 1881–1886. - PubMed
-
- Hiuge‐Shimizu A, Kishida K, Funahashi T, et al Absolute value of visceral fat area measured on computed tomography scans and obesity‐related cardiovascular risk factors in large‐scale Japanese general population (the VACATION‐J study). Ann Med 2012; 44: 82–92. - PubMed
15 HYPERTENSION ASSOCIATED WITH DIABETES
-
- Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, et al The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res 2019; 42: 1235–1481. - PubMed
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, Kato M, et al Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J‐DOIT3): an open‐label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabet Endcrinol 2017; 5: 951–964 [level 1]. - PubMed
-
- Baba S. Nifedipine and enalapril equally reduce the progression of nephropathy in hypertensive type 2 diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2001; 54: 191–201 [level 1]. - PubMed
-
- Berl T, Hunsicker LG, Lewis JB, et al Cardiovascular outcomes in the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial of patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Ann Intern Med 2003; 138: 542–549 [level 1]. - PubMed
16 DYSLIPIDEMIA ASSOCIATED WITH DIABETES
-
- Sacks FM, Hermans MP, Fioretto P, et al Association between plasma triglycerides and high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol and microvascular kidney disease and retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a global case‐control study in 13 countries. Circulation 2014; 129: 999–1008. - PubMed
-
- Heilbronn LK, Noakes M, Clifton PM. Effect of energy restriction, weight loss, and diet composition on plasma lipids and glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999; 22: 889–895 [level 2]. - PubMed
17 IMPAIRED GLUCOSE METABOLISM IN PREGNANCY
-
- Ray JG, O'Brien TE, Chan WS. Preconception care and the risk of congenital anomalies in the offspring of women with diabetes mellitus: a meta‐analysis. QJM 2001; 94: 435–444 [level 2]. - PubMed
-
- Griffin ME, Coffey M, Johnson H, et al Universal vs. risk factor‐based screening for gestational diabetes mellitus: detection rates, gestation at diagnosis and outcome. Diabet Med 2000; 17: 26–32. - PubMed
18 PEDIATRIC/ADOLESCENT DIABETES
-
- ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes 2014. Nankodo, Tokyo, 2015.
-
- Ascerini C, Craig ME, de Beaufort C, et al ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2014 compendium. Introduction. Pediatr Diabetes 2014; 15(Suppl 20): 1–3. - PubMed
-
- Craig ME, Jefferies C, Dabelea D, et al ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2014 compendium. Definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adlescents. Pediatr Diabetes 2014; 15(Suppl 20): 4–17. - PubMed
-
- White NH, Cleary PA, Dahms W, et al Beneficial effects of intensive therapy of diabetes during adolescence: outcomes after the conclusion of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). J Pediatr 2001; 139: 804–812. - PubMed
-
- Urakami T, Morimoto S, Nitadori Y, et al Urine glucose screening program at schools in Japan to detect children with diabetes and its outcome: Incidence and clinical characteristics of childhood type 2 diabetes in Japan. Pediatr Res 2007; 61: 141–145. - PubMed
20 ACUTE METABOLIC COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES, SICK DAYS, AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES
-
- Nyenwe EA, Kitabchi AE. Evidence‐based management of hyperglycemic emergencies in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2011; 94: 340–351. - PubMed
-
- Wolfsdorf JI, Allgrove J, Craig ME, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Pediatr Diabetes 2014; 15(Suppl 20): 154–179. - PubMed
-
- Jeffrey A, Kraut MD, Nicolaos E, et al Lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 2309–2319. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association . Standards of medical care in diabetes–2018. Diabetes Care 2018; 41: S1–S157. - PubMed
21 PREVENTION OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
-
- Doi Y, Ninomiya T, Hata J, et al Two risk score models for predicting incident type 2 diabetes in Japan. Diabet Med 2012; 29: 107–114. - PubMed
-
- Heianza Y, Arase Y, Hsieh SD, et al Development of a new scoring system for predicting the 5 year incidence of type 2 diabetes in Japan: the Toranomon Hospital Health Management Center Study 6 (TOPICS 6). Diabetologia 2012; 55: 3213–3223. - PubMed
APPENDIX 1. DIABETES AND CANCER
-
- Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta‐analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005; 97: 1679–1687. - PubMed
-
- Larsson SC, Orsini N, Brismar K, et al Diabetes mellitus and risk of bladder cancer: a meta‐analysis. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 2819–2823. - PubMed
-
- Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, et al Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60: 207–221. - PubMed
APPENDIX 2. DIABETES AND BONE MINERAL METABOLISM
-
- Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Life Science Publishing.
-
- Janghorbani M, Van Dam RM, Willett WC, et al Systematic review of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of fracture. Am J Epidemiol 2007; 166: 495–505. - PubMed
-
- Vestergaard P. Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a meta‐analysis. Osteoporos Int 2007; 18: 427–444. - PubMed
APPENDIX 3. PANCREAS/ISLET TRANSPLANTATION
-
- Saito T, Gotoh M, Satomi S, et al Islet transplantation using donors after cardiac death: report of the Japan Islet Transplantation Registry. Transplantation 2010; 90: 740–747. - PubMed
-
- Hering BJ, Kandaswamy R, Ansite JD, et al Single‐donor, marginal‐dose islet transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes. JAMA 2005; 293: 830–835. - PubMed
APPENDIX 4. LARGE‐SCALE CLINICAL TRIALS IN JAPANESE PATIENTS WITH DIABETES
-
- Ueki K, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J‐DOIT3): an open‐label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

