UV-LED disinfection of Coronavirus: Wavelength effect
- PMID: 33022467
- PMCID: PMC7521879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.112044
UV-LED disinfection of Coronavirus: Wavelength effect
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "UV-LED disinfection of Coronavirus: wavelength effect" [Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 212 (2020) 112044-end page].J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021 Mar;216:112132. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112132. Epub 2021 Feb 4. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021. PMID: 33550220 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
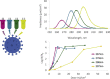
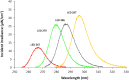
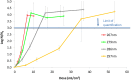
UV light-emitting diodes (UV LEDs) are an emerging technology and a UV source for pathogen inactivation, however low UV-LED wavelengths are costly and have low fluence rate. Our results suggest that the sensitivity of human Coronavirus (HCoV-OC43 used as SARS-CoV-2 surrogate) was wavelength dependent with 267 nm ~ 279 nm > 286 nm > 297 nm. Other viruses showed similar results, suggesting UV LED with peak emission at ~286 nm could serve as an effective tool in the fight against human Coronaviruses.
Keywords: COVID19; Corona; Coronavirus; SARS; UV-LEDs; Wavelength.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Infection Prevention Precautions. 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/transmission-of-sars-c...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

