Caryocar brasiliense Cambess. Pulp Oil Supplementation Reduces Total Cholesterol, LDL-c, and Non-HDL-c in Animals
- PMID: 33022905
- PMCID: PMC7582708
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25194530
Caryocar brasiliense Cambess. Pulp Oil Supplementation Reduces Total Cholesterol, LDL-c, and Non-HDL-c in Animals
Abstract
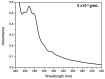
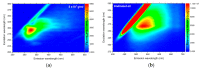
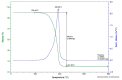
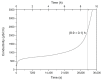
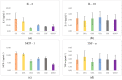
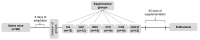
The fruit of Caryocar brasiliense Cambess. is a source of oil with active compounds that are protective to the organism. In our work, we analyzed the physicochemical characteristics and evaluated the effects of supplementation with C. brasiliense oil in an animal model. We characterized the oil by indices of quality and identity, optical techniques of absorption spectroscopy in the UV-Vis region and fluorescence, and thermogravimetry/derived thermogravimetry (TG/DTG). For the animal experiment, we utilized mice (Mus musculus) supplemented with lipidic source in different dosages. The results demonstrated that C. brasiliense oil is an alternative source for human consumption and presents excellent oxidative stability. Primarily, it exhibited oleic MFA (53.56%) and palmitic SFA (37.78%). The oil level of tocopherols and tocotrienols was superior to the carotenoids. The supplementation with C. brasiliense oil reduced the levels of total cholesterol, LDL-c, and non-HDL-c. Regarding visceral fats and adiposity index, the treatment synergically supplemented with olive oil and C. brasiliense oil (OO + CO) obtained the best result. Therefore, C. brasiliense oil is a high quality product for consumption. Its supplementation promotes beneficial effects mainly on the lipidic profile.
Keywords: fatty acids; natural products; pequi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential of Whole Pequi (Caryocar spp.) Fruit-Pulp, Almond, Oil, and Shell-as a Medicinal Food.J Med Food. 2019 Sep;22(9):952-962. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.0149. Epub 2019 May 10. J Med Food. 2019. PMID: 31074677
-
Discrimination of pulp oil and kernel oil from pequi (Caryocar brasiliense) by fatty acid methyl esters fingerprinting, using GC-FID and multivariate analysis.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Nov 18;63(45):10064-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03699. Epub 2015 Nov 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26506457
-
Caryocar brasiliense oil improves cardiac function by increasing Serca2a/PLB ratio despite no significant changes in cardiovascular risk factors in rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Feb 8;16(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0422-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28179001 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Challenges of the Extraction of Carotenoids and Fatty Acids from Pequi (Caryocar brasiliense) Oil.Foods. 2023 May 6;12(9):1907. doi: 10.3390/foods12091907. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37174442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Pequi Oil (Caryocar brasiliense): A Systematic Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;17(1):11. doi: 10.3390/ph17010011. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38275996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of diet based nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rodent models: Histological and biochemical outcomes.Histol Histopathol. 2022 Sep;37(9):813-824. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-462. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35475465 Review.
-
Characterization of Buriti (Mauritia flexuosa) Pulp Oil and the Effect of Its Supplementation in an In Vivo Experimental Model.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 19;14(12):2547. doi: 10.3390/nu14122547. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35745276 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Efficacy Evaluation of Innovative Cosmetic Formulations with Caryocar brasiliense Fruit Pulp Oil Encapsulated in Freeze-Dried Liposomes.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 27;16(5):595. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050595. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794256 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Grape Seed Oil, Linseed Oil, and a Blend: In Vivo Effects of Supplementation.Foods. 2024 Jul 20;13(14):2283. doi: 10.3390/foods13142283. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39063367 Free PMC article.
-
Pequi Fruit Extract Increases Antioxidant Enzymes and Reduces Oxidants in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Feb 28;11(3):474. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030474. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Redondo-Cuevas L., Castellano G., Torrens F., Raikos V. Revealing the relationship between vegetable oil composition and oxidative stability: A multifactorial approach. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018;66:221–229. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2017.12.027. - DOI
-
- Castelo-Branco V.N., Santana I., Di-Sarli V.O., Freitas S.P., Torres A.G. Antioxidant capacity is a surrogate measure of the quality and stability of vegetable oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016;118:224–235. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201400299. - DOI
-
- Codex Alimentarius Standard For Named Vegetable Oils Codex Stan 210-1999 Adopted. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 1990:1–13.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

