PGC-1α in Disease: Recent Renal Insights into a Versatile Metabolic Regulator
- PMID: 33022986
- PMCID: PMC7601329
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9102234
PGC-1α in Disease: Recent Renal Insights into a Versatile Metabolic Regulator
Abstract
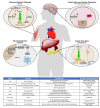
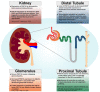
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1 alpha (PGC-1α) is perhaps best known as a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and function. However, by virtue of its interactions as a coactivator for numerous nuclear receptors and transcription factors, PGC-1α also regulates many tissue-specific tasks that include adipogenesis, angiogenesis, gluconeogenesis, heme biosynthesis, thermogenesis, and cellular protection against degeneration. Knowledge about these functions continue to be discovered with ongoing research. Unsurprisingly, alterations in PGC-1α expression lead to a range of deleterious outcomes. In this review, we provide a brief background on the PGC-1 family with an overview of PGC-1α's roles as an adaptive link to meet cellular needs and its pathological consequences in several organ contexts. Among the latter, kidney health is especially reliant on PGC-1α. Thus, we discuss here at length how changes in PGC-1α function impact the states of renal cancer, acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), as well as emerging data that illuminate pivotal roles for PGC-1α during renal development. We survey a new intriguing association of PGC-1α function with ciliogenesis and polycystic kidney disease (PKD), where recent animal studies revealed that embryonic renal cyst formation can occur in the context of PGC-1α deficiency. Finally, we explore future prospects for PGC-1α research and therapeutic implications for this multifaceted coactivator.
Keywords: AKI; CKD; PGC-1α, disease; PKD; cancer; cilia; cystogenesis; kidney; nephron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) in Kidney Disease.Semin Nephrol. 2018 Mar;38(2):121-126. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2018.01.003. Semin Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29602395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of PGC-1α and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Kidney Diseases.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 24;10(2):347. doi: 10.3390/biom10020347. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32102312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) overexpression alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress after acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):358-367. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2035764. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35225153 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of PGC-1α and its therapeutic potential.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Jun;30(6):322-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2009.03.006. Epub 2009 May 14. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19446346 Review.
-
PGC-1α deficiency causes spontaneous kidney inflammation and increases the severity of nephrotoxic AKI.J Pathol. 2019 Sep;249(1):65-78. doi: 10.1002/path.5282. Epub 2019 Jun 12. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30982966
Cited by
-
Hif-2α regulates lipid metabolism in alcoholic fatty liver disease through mitophagy.Cell Biosci. 2022 Dec 7;12(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00889-1. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36476627 Free PMC article.
-
4-Octyl itaconate attenuates renal tubular injury in db/db mice by activating Nrf2 and promoting PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2403653. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2403653. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39291665 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice.Open Life Sci. 2023 Feb 23;18(1):20220570. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0570. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36852401 Free PMC article.
-
Insufficient sleep disrupts glucose metabolism during pregnancy by inhibiting PGC-1α.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Nov;10(22):1241. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5551. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36544637 Free PMC article.
-
Esrrγa regulates nephron and ciliary development by controlling prostaglandin synthesis.Development. 2023 May 15;150(10):dev201411. doi: 10.1242/dev.201411. Epub 2023 May 26. Development. 2023. PMID: 37232416 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

