Differences in breast cancer risk after benign breast disease by type of screening diagnosis
- PMID: 33023825
- PMCID: PMC7770442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.09.005
Differences in breast cancer risk after benign breast disease by type of screening diagnosis
Abstract
Introduction: We aimed to assess differences in breast cancer risk across benign breast disease diagnosed at prevalent or incident screens.
Materials and methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study with data from 629,087 women participating in a long-standing population-based breast cancer screening program in Spain. Each benign breast disease was classified as non-proliferative, proliferative without atypia, or proliferative with atypia, and whether it was diagnosed in a prevalent or incident screen. We used partly conditional Cox hazard regression to estimate the adjusted hazard ratios of the risk of breast cancer.
Results: Compared with women without benign breast disease, the risk of breast cancer was significantly higher (p-value = 0.005) in women with benign breast disease diagnosed in an incident screen (aHR, 2.67; 95%CI: 2.24-3.19) than in those with benign breast disease diagnosed in a prevalent screen (aHR, 1.87; 95%CI: 1.57-2.24). The highest risk was found in women with a proliferative benign breast disease with atypia (aHR, 4.35; 95%CI: 2.09-9.08, and 3.35; 95%CI: 1.51-7.40 for those diagnosed at incident and prevalent screens, respectively), while the lowest was found in women with non-proliferative benign breast disease (aHR, 2.39; 95%CI: 1.95-2.93, and 1.63; 95%CI: 1.32-2.02 for those diagnosed at incident and prevalent screens, respectively).
Conclusion: Our study showed that the risk of breast cancer conferred by a benign breast disease differed according to type of screen (prevalent or incident). To our knowledge, this is the first study to analyse the impact of the screening type on benign breast disease prognosis.
Keywords: Benign breast disease; Breast neoplasms; Early cancer detection; Risk factors.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None declared.
Figures
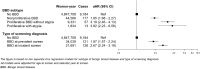



References
-
- Carter C.L., Corle D.K., Micozzi M.S., Schatzkin A., Taylor P.R. A prospective study of the development of breast cancer in 16,692 women with benign breast disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1988;128(3):467–477. - PubMed
-
- Hartmann L.C., Sellers T.A., Frost M.H., Lingle W.L., Degnim A.C., Ghosh K. Benign breast disease and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(3):229–237. - PubMed
-
- Castells X., Domingo L., Corominas J.M., Tora-Rocamora I., Quintana M.J., Bare M. Breast cancer risk after diagnosis by screening mammography of nonproliferative or proliferative benign breast disease: a study from a population-based screening program. Breast Canc Res Treat. 2015;149(1):237–244. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Page D.L., Dupont W.D., Rogers L.W., Rados M.S. Atypical hyperplastic lesions of the female breast. A long-term follow-up study. Cancer. 1985;55(11):2698–2708. - PubMed
-
- Dupont W.D., Page D.L. Risk factors for breast cancer in women with proliferative breast disease. N Engl J Med. 1985;312(3):146–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

