Combination Treatment with Sodium Nitrite and Isoquercetin on Endothelial Dysfunction among Patients with CKD: A Randomized Phase 2 Pilot Trial
- PMID: 33023894
- PMCID: PMC7646238
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.02020220
Combination Treatment with Sodium Nitrite and Isoquercetin on Endothelial Dysfunction among Patients with CKD: A Randomized Phase 2 Pilot Trial
Abstract
Background and objectives: Endothelial dysfunction is common among patients with CKD. We tested the efficacy and safety of combination treatment with sodium nitrite and isoquercetin on biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction in patients with CKD.
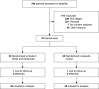
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 pilot trial enrolled 70 patients with predialysis CKD. Thirty-five were randomly assigned to combination treatment with sodium nitrite (40 mg twice daily) and isoquercetin (225 mg once daily) for 12 weeks, and 35 were randomly assigned to placebo. The primary outcome was mean change in flow-mediated vasodilation over the 12-week intervention. Secondary and safety outcomes included biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress as well as kidney function, methemoglobin, and adverse events. Intention-to-treat analysis was conducted.
Results: Baseline characteristics, including age, sex, race, cigarette smoking, history of hypertension and diabetes, use of renin-angiotensin system blockers, BP, fasting glucose, lipid profile, kidney function, urine albumin-creatinine ratio, and endothelial biomarkers, were comparable between groups. Over the 12-week intervention, flow-mediated vasodilation increased 1.1% (95% confidence interval, -0.1 to 2.3) in the treatment group and 0.3% (95% confidence interval, -0.9 to 1.5) in the placebo group, and net change was 0.8% (95% confidence interval, -0.9 to 2.5). In addition, changes in biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction (vascular adhesion molecule-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, E-selectin, vWf, endostatin, and asymmetric dimethylarginine), inflammation (TNF-α, IL-6, C-reactive protein, IL-1 receptor antagonist, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1), and oxidative stress (oxidized LDL and nitrotyrosines) were not significantly different between the two groups. Furthermore, changes in eGFR, urine albumin-creatinine ratio, methemoglobin, and adverse events were not significantly different between groups.
Conclusions: This randomized phase 2 pilot trial suggests that combination treatment with sodium nitrite and isoquercetin did not significantly improve flow-mediated vasodilation or other endothelial function biomarkers but also did not increase adverse events compared with placebo among patients with CKD.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: Nitrite, Isoquercetin, and Endothelial Dysfunction (NICE), NCT02552888.
Keywords: chronic inflammation; chronic kidney disease; endothelial dysfunction; isoquercetin; oxidative stress; sodium nitrite.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Coresh J, Turin TC, Matsushita K, Sang Y, Ballew SH, Appel LJ, Arima H, Chadban SJ, Cirillo M, Djurdjev O, Green JA, Heine GH, Inker LA, Irie F, Ishani A, Ix JH, Kovesdy CP, Marks A, Ohkubo T, Shalev V, Shankar A, Wen CP, de Jong PE, Iseki K, Stengel B, Gansevoort RT, Levey AS; CKD Prognosis Consortium : Decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate and subsequent risk of end-stage renal disease and mortality. JAMA 311: 2518–2531, 2014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, Gansevoort RT; Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium : Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet 375: 2073–2081, 2010. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manjunath G, Tighiouart H, Ibrahim H, MacLeod B, Salem DN, Griffith JL, Coresh J, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ: Level of kidney function as a risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular outcomes in the community. J Am Coll Cardiol 41: 47–55, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous