Long-term metformin adherence in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study
- PMID: 33023898
- PMCID: PMC7539607
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001537
Long-term metformin adherence in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study
Abstract
Introduction: To investigate long-term metformin adherence in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study (DPPOS) by examining: (1) predictors of long-term adherence to study metformin and (2) whether metformin adherence was associated with incident type 2 diabetes.
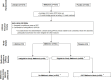
Research design and methods: DPPOS was an open-label continuation of the randomized clinical trial (Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP)) in which eligible participants randomized to the metformin group were offered study metformin and followed over 11 years. A brief structured adherence interview was administered semiannually. Metformin adherence was assessed by pill counts. Predictors of metformin adherence were examined in multivariate regression models. Incident diabetes associated with metformin adherence and other variables was assessed in Cox proportional hazards models.
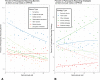
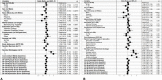
Results: Of 868 participants eligible to continue taking study metformin, 664 (76%) took at least some metformin over 11 years, with 478 of them reporting problems with adherence. DPPOS cumulative adherence showed significant associations of higher adherence (≥80%) with early adherence at 3 months in DPP (p<0.001) and lower depression scores during DPPOS (p<0.001); significant differences were also seen by race/ethnicity (p<0.004). Predicting adherence by multivariate modeling showed odds of adherence significantly lower for Black participants and for participants reporting more than one barrier. Odds for adherence were significantly higher for those adherent early in DPP and those reporting at least one planned strategy to improve adherence. Higher metformin adherence was significantly associated with a lower diabetes risk (p=0.04), even after adjustment for demographic variables, depression, and anxiety scores.
Conclusions: In this long-term diabetes prevention study, early metformin adherence and planned strategies to promote adherence improved long-term adherence over 11 years; higher adherence to metformin was related to lower diabetes incidence. Incorporating strategies to promote adherence when initially prescribing metformin and counseling to support adherence over time are warranted.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; medication adherence; metformin; preventive medicine; type 2.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group Long-Term effects of lifestyle intervention or metformin on diabetes development and microvascular complications over 15-year follow-up: the diabetes prevention program outcomes study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2015;3:866–75. 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00291-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK048412/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048375/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048468/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048437/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048407/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK111022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048339/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048514/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048485/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048443/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048380/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048400/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048489/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
