Cross-reactive memory T cells and herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33024281
- PMCID: PMC7537578
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-020-00460-4
Cross-reactive memory T cells and herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
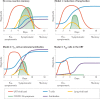
Immunity is a multifaceted phenomenon. For T cell-mediated memory responses to SARS-CoV-2, it is relevant to consider their impact both on COVID-19 disease severity and on viral spread in a population. Here, we reflect on the immunological and epidemiological aspects and implications of pre-existing cross-reactive immune memory to SARS-CoV-2, which largely originates from previous exposure to circulating common cold coronaviruses. We propose four immunological scenarios for the impact of cross-reactive CD4+ memory T cells on COVID-19 severity and viral transmission. For each scenario, we discuss its implications for the dynamics of herd immunity and on projections of the global impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the human population, and assess its plausibility. In sum, we argue that key potential impacts of cross-reactive T cell memory are already incorporated into epidemiological models based on data of transmission dynamics, particularly with regard to their implications for herd immunity. The implications of immunological processes on other aspects of SARS-CoV-2 epidemiology are worthy of future study.
Conflict of interest statement
A.S. is a consultant for Gritstone, Flow Pharma, Merck and Avalia. S.C. is a consultant for Avalia and JPMorgan. M.L. discloses honoraria/consulting from Merck, Affinivax, Sanofi-Pasteur and Antigen Discovery; research funding (institutional) from Pfizer; and unpaid scientific advice to Janssen, AstraZeneca, 1DaySooner and Covaxx (United Biomedical). Y.H.G. discloses consulting from Merck and Quidel; and research funding (institutional) from Pfizer.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

