Valeric Acid Suppresses Liver Cancer Development by Acting as a Novel HDAC Inhibitor
- PMID: 33024815
- PMCID: PMC7520432
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.08.017
Valeric Acid Suppresses Liver Cancer Development by Acting as a Novel HDAC Inhibitor
Abstract
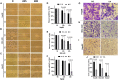
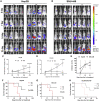
Liver cancer is the fastest growing cause of cancer deaths in the United States due to its aggressiveness and lack of effective therapies. The current preclinical study examines valeric acid (pentanoic acid [C5H10O2]), one of the main compounds of valerian root extract, for its therapeutic use in liver cancer treatment. Anticancer efficacy of valeric acid was tested in a series of in vitro assays and orthotopic xenograft mouse models. The molecular target of valeric acid was also predicted, followed by functional confirmation. Valeric acid has a broad spectrum of anticancer activity with specifically high cytotoxicity for liver cancer in cell proliferation, colony formation, wound healing, cell invasion, and 3D spheroid formation assays. Mouse models further demonstrate that systematic administration of lipid-based nanoparticle-encapsulated valeric acid significantly reduces the tumor burden and improves survival rate. Histone deacetylase (HDAC)-inhibiting functions of valeric acid are also revealed by a structural target prediction tool and HDAC activity assay. Further transcriptional profiling and network analyses illustrate that valeric acid affects several cancer-related pathways that may induce apoptosis. In summary, we demonstrate for the first time that valeric acid suppresses liver cancer development by acting as a potential novel HDAC inhibitor, which warrants further investigation on its therapeutic implications.
Keywords: 3D formation; HDACi; apoptosis; cell migration; cell proliferation; colony formation; hepatocellular carcinoma; lipid nanoparticle; mouse model; valeric acid.
© 2020.
Figures





References
-
- Niino M., Matsuda T. Incidence rates of liver cancer in the world from the Cancer Incidence in Five Continents XI. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;49:693–694. - PubMed
-
- Prevention of Infection Related Cancer (PIRCA) Group, Specialized Committee of Cancer Prevention and Control, Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. Non-communicable & Chronic Disease Control and Prevention Society, Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. Health Communication Society, Chinese Preventive Medicine Association [Strategies of primary prevention of liver cancer in China: expert consensus (2018)] Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;53:36–44. - PubMed
-
- Hobbs C. Phu: valerian and other anti-hysterics in European and American medicine (1733-1936) Pharm. Hist. 1990;32:132–137. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

