Individualized mechanical ventilation in a shared ventilator setting: limits, safety and technical details
- PMID: 33025322
- PMCID: PMC7537776
- DOI: 10.1007/s10877-020-00596-7
Individualized mechanical ventilation in a shared ventilator setting: limits, safety and technical details
Abstract
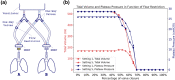
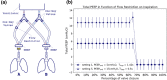
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in an increased need for ventilators. The potential to ventilate more than one patient with a single ventilator, a so-called split ventilator setup, provides an emergency solution. Our hypothesis is that ventilation can be individualized by adding a flow restrictor to limit tidal volumes, add PEEP, titrate FiO2 and monitor ventilation. This way we could enhance optimization of patient safety and clinical applicability. We performed bench testing to test our hypothesis and identify limitations. We performed a bench testing in two test lungs: (1) determine lung compliance (2) determine volume, plateau pressure and PEEP, (3) illustrate individualization of airway pressures and tidal volume with a flow restrictor, (4a) illustrate that PEEP can be applied and individualized (4b) create and measure intrinsic PEEP (4c and d) determine PEEP as a function of flow restriction, (5) individualization of FiO2. The lung compliance varied between 13 and 27 mL/cmH2O. Set ventilator settings could be applied and measured. Extrinsic PEEP can be applied except for settings with a large expiratory time. Volume and pressure regulation is possible between 70 and 39% flow restrictor valve closure. Flow restriction in the tested circuit had no effect on the other circuit or on intrinsic PEEP. FiO2 could be modulated individually between 0.21 and 0.8 by gradually adjusting the additional flow, and minimal affecting FiO2 in the other circuit. Tidal volumes, PEEP and FiO2 can be individualized and monitored in a bench testing of a split ventilator. In vivo research is needed to further explore the clinical limitations and outcomes, making implementation possible as a last resort ventilation strategy.
Keywords: ARDS; Bench testing; COVID-19; Individualized split ventilation.
© 2020. Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic . Increased transmission in the EU/EEA and the UK – seventh update, 25 March 2020. Stockholm: ECDC; 2020. p. 2020.
-
- Branson RD, Rubinson L, One ventilator multiple patients—what the data really supports. Resuscitation; 2008. 79(1):171-172; author reply 172-173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

