Yoga effectively reduces fatigue and symptoms of depression in patients with different types of cancer
- PMID: 33026490
- PMCID: PMC8062403
- DOI: 10.1007/s00520-020-05794-2
Yoga effectively reduces fatigue and symptoms of depression in patients with different types of cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Examine the effects of an 8-week yoga therapy on fatigue in patients with different types of cancer.
Methods: A total of 173 cancer patients suffering from mild to severe fatigue were randomly allocated to yoga intervention (n = 84) (IG) versus waitlist control group (CG) (n = 88). Yoga therapy consisted of eight weekly sessions with 60 min each. The primary outcome was self-reported fatigue symptoms. Secondary outcomes were symptoms of depression and quality of life (QoL). Data were assessed using questionnaires before (T0) and after yoga therapy for IG versus waiting period for CG (T1).
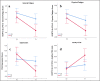
Results: A stronger reduction of general fatigue (P = .033), physical fatigue (P = .048), and depression (P < .001) as well as a stronger increase in QoL (P = .002) was found for patients who attended 7 or 8 sessions compared with controls. Within the yoga group, both higher attendance rate and lower T0-fatigue were significant predictors of lower T1-fatigue (P ≤ .001). Exploratory results revealed that women with breast cancer report a higher reduction of fatigue than women with other types of cancer (P = .016) after yoga therapy.
Conclusion: The findings support the assumption that yoga therapy is useful to reduce cancer-related fatigue, especially for the physical aspects of fatigue. Women with breast cancer seem to benefit most, and higher attendance rate results in greater reduction of fatigue.
Trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register DRKS00016034.
Keywords: Complementary alternative medicine; Depression; Fatigue; Mind-body intervention; Quality of life; Yoga.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 2018;391(10125):1023–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger AM, Mooney K, Alvarez-Perez A, Breitbart WS, Carpenter KM, Cella D, Cleeland C, Dotan E, Eisenberger MA, Escalante CP, Jacobsen PB, Jankowski C, LeBlanc T, Ligibel JA, Loggers ET, Mandrell B, Murphy BA, Palesh O, Pirl WF, Plaxe SC, Riba MB, Rugo HS, Salvador C, Wagner LI, Wagner-Johnston ND, Zachariah FJ, Bergman MA, Smith C, National comprehensive cancer network Cancer-related fatigue, version 2.2015. J Natl Compr Canc Ne. 2015;13(8):1012–1039. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2015.0122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Curt GA, Breitbart W, Cella D, Groopman JE, Horning SJ, Itri LM, Johnson DH, Miaskowski C, Scherr SL, Portenoy RK, Vogelzang NJ. Impact of cancer-related fatigue on the lives of patients: new findings from the Fatigue Coalition. Oncologist. 2000;5(5):353–360. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.5-5-353. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

