Substantial Decline in Use of HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis Following Introduction of COVID-19 Physical Distancing Restrictions in Australia: Results From a Prospective Observational Study of Gay and Bisexual Men
- PMID: 33027151
- PMCID: PMC7727320
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002514
Substantial Decline in Use of HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis Following Introduction of COVID-19 Physical Distancing Restrictions in Australia: Results From a Prospective Observational Study of Gay and Bisexual Men
Abstract
Background: In response to the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, Australia introduced public health and physical distancing restrictions in late March 2020. We investigated the impact of these restrictions on HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) use among Australian gay and bisexual men (GBM).
Methods: Participants in an ongoing online cohort study previously reported PrEP use from 2014 to 2019. In April 2020, 847 HIV-negative and untested participants completed questionnaires assessing changes in PrEP use as a result of COVID-19 public health measures. Binary logistic multiple regression was used to estimate adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) to compare changes in PrEP use behaviors.
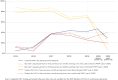
Results: Among 847 men, mean age was 44.1 years (SD: 12.7). PrEP use rose from 4.9% in 2015 to 47.2% in 2020. Among those, 41.8% (n = 167) discontinued PrEP use during COVID-19 restrictions. Discontinuing PrEP during COVID-19 restrictions was independently associated with being less likely to have recently tested for HIV (aOR: 0.17; 95% CI: 0.09 to 0.34; P < 0.001) and less likely to report sex with casual partners (aOR: 0.28; 95% CI: 0.14 to 0.54; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: By April 2020, following the introduction of COVID-19 restrictions, GBM dramatically reduced PrEP use, coinciding with a reduction in sexual activity. Longer-term impacts of COVID-19 restrictions on sexual behaviors among GBM need to be monitored because they may foreshadow fluctuations in prevention coverage and risk of HIV infection. Our findings indicate a potential need for clear, targeted information about resumption of PrEP and on-demand optimal dosing regimens in response to ongoing changes in restrictions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Considerations in Adjusting Public Health and Social Measures in the Context of COVID-19: Interim Guidance: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- Commonwealth of Australia as represented by the Department of Health. COVID-19 National Incident Room Surveillance Team. COVID-19, Australia: Epidemiology Report 14 (Reporting Week Ending 23:59 AEST 3 May 2020): Communicable diseases intelligence; 2020:44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous