Ruptured liver abscess presenting as pneumoperitoneum caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: a case report
- PMID: 33028298
- PMCID: PMC7542763
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-020-00858-w
Ruptured liver abscess presenting as pneumoperitoneum caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: a case report
Abstract
Background: Spontaneous gas-forming pyogenic liver abscess (GFPLA) is a rare complication with a high fatality rate in spite of aggressive management. Clinical spectrum of GFPLA can mimic hollow viscus perforation as it usually accompanied by pneumoperitoneum and peritonitis. Up to now, GFPLA has not been well studied in Vietnam.
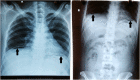
Case presentation: We reported here a case with pneumoperitoneum caused by ruptured liver abscess in a 41-year-old man with a history of treated duodenal ulcer and uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus. He had an epigastric pain associated with a high fever. Patient was diagnosed peritonitis and pneumoperitoneum presumed to be secondary to perforation of a hollow viscus and subjected to emergency laparotomy. We did not find any gastrointestinal perforation. Surprisingly, we detected a 4 cm × 4 cm pus-containing abscess in the left liver lobe of the liver. The abscess was ruptured. Pus was running into abdominal cavity through one hole. The abscess and abdominal cavities were cleaned up and abscess and abdominal drainages were performed. K. pneumoniae was isolated from culture of the abscess. The histopathological examination of the abscess did not yield any evidence of malignancy. Blood glucose levels were controlled. Antibiotic therapy was used according to antibiogram. A reassessment chest X-ray showed no air-fluid level or subdiaphragmatic air by the hospital day 14. Patient eventually made a full recovery and was discharged home 23 days after the operation.
Conclusions: Ruptured GFPLA is a life-threatening complication. It is usually accompanied by peritonitis and pneumoperitoneum and can imitate hollow viscous perforation. In these cases, CT scan should be performed whenever it is possible to make a correct diagnosis. When the abscess has small size, partial hepatectomy might not be necessary and could be replaced by a careful cleaning and drainage of the abscess. Patient could show a good postoperative recovery following an appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Keywords: Case report; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Pneumoperitoneum; Ruptured liver abscess.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unusual pneumoperitoneum secondary to ruptured liver abscess-A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021 Mar;80:105499. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.12.089. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33609947 Free PMC article.
-
Ruptured hepatic abscess mimicking perforated viscus.Int J Infect Dis. 2008 Nov;12(6):e95-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.06.005. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Int J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18768341
-
An unusual presentation of spontaneous pneumoperitoneum secondary to the rupture of a gas-containing pyogenic liver abscess: report of a case.Surg Today. 1994;24(1):63-6. doi: 10.1007/BF01676888. Surg Today. 1994. PMID: 8054779
-
Liver abscess in the caudate lobe caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: a rare case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09569-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39030483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monomicrobial Klebsiella pneumoniae Necrotizing Fasciitis With Liver Abscess: A Case Report and Literature Review.Ann Plast Surg. 2017 Mar;78(3 Suppl 2):S28-S31. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000001001. Ann Plast Surg. 2017. PMID: 28177973 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful hepatic resection for invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae large multiloculated liver abscesses with percutaneous drainage failure: A case report.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 6;9:1092879. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1092879. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36687430 Free PMC article.
-
Ruptured Pyogenic Liver Abscess as an Uncommon Cause of Pneumoperitoneum.J Belg Soc Radiol. 2022 Apr 5;106(1):13. doi: 10.5334/jbsr.2784. eCollection 2022. J Belg Soc Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35480336 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal systemic emphysematous infection caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Mar 16;10(8):2610-2615. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2610. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35434061 Free PMC article.
-
Emphysematous liver abscess: Variable clinical presentations, management challenges and outcomes-a case series.Turk J Surg. 2024 Sep 30;40(3):247-255. doi: 10.47717/turkjsurg.2024.6436. eCollection 2024 Sep. Turk J Surg. 2024. PMID: 39917401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiou Y-W, Lin Y-T. Gas-forming Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in a patient without diabetes. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2014;48. 10.1016/j.jmii.2014.05.005. - PubMed
-
- Huy H, Tri L, Minh L, Vinh N. Intra-abdominal ruptured liver abscess: computed tomography and clinical features. Med Imaging Radiol. 2019;7:3. doi: 10.7243/2054-1945-7-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical