Asymptomatic Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-associated Myocarditis
- PMID: 33028770
- PMCID: PMC7946516
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5412-20
Asymptomatic Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-associated Myocarditis
Abstract
We herein report the case of a 75-year-old man with asymptomatic immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-associated myocarditis diagnosed on the basis of elevated levels of creatine kinase (CK), CK-myocardial band and troponin I (TNI). He was suspected of being complicated with myasthenia gravis (MG). High-dose prednisolone (PSL) is associated with a risk of MG exacerbation; therefore, PSL therapy was gradually increased from 5 mg/day to 20 mg/day, which resulted in the normalization of the TNI level, and no PSL-related side effects occurred. MG easily complicates myocarditis as an immune-related adverse event; thus, the treatment plan should be carefully considered.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitor; immune-related adverse event; myasthenia gravis; myocarditis; prednisolone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




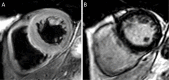
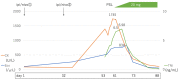
References
-
- Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med 378: 158-168, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Love VA, Grabie N, Duramad P, et al. . CTLA-4 ablation and interleukin-12 driven differentiation synergistically augment cardiac pathogenicity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Circ Res 101: 248-257, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira VM, Schulz-Menger J, Holmvang G, et al. . Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in nonischemic myocardial inflammation. Expert recommendations. J Am Coll Cardiol 72: 3158-3176, 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

