Effective Use of Keishibukuryogan in Subcutaneous Hematoma after Implantable Cardiac Device Surgery in Two Cases
- PMID: 33028772
- PMCID: PMC7990628
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5677-20
Effective Use of Keishibukuryogan in Subcutaneous Hematoma after Implantable Cardiac Device Surgery in Two Cases
Abstract
Keishibukuryogan is a Kampo medicine that induces vasodilation and improves the blood flow velocity in subcutaneous blood vessels. We herein report two cases in which keishibukuryogan completely diminished subcutaneous hematoma after cardiac resynchronization therapy pacemaker implantation and defibrillator battery replacement within a month. Keishibukuryogan can be a good option for treating or preventing subcutaneous hematoma after surgical procedures for devices.
Keywords: Kampo; Kampo medicine; herbal medicine; implantable cardiac device surgery; keishibukuryogan; subcutaneous hematoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





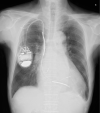


References
-
- Sridhar AR, Yarlagadda V, Yeruva MR, et al. . Impact of haematoma after pacemaker and CRT device implantation on hospitalization costs, length of stay, and mortality: a population-based study. Europace 17: 1548-1554, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Turagam MK, Nagarajan DV, Bartus K, et al. . Use of a pocket compression device for the prevention and treatment of pocket hematoma after pacemaker and defibrillator implantation (STOP-HEMATOMA-I). J Interv Card Electrophysiol 49: 197-204, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Wiegand UK, Lejeune D, Bogushewaski F, et al. . Pocket hematoma after pacemaker or implantable cardioverter defibrillator surgery: influence of patient morbidity, operation strategy, and perioperative antiplatelet/anticoagulation therapy. CHEST 126: 1177-1186, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Demir GG, Guier GB, Guler E, et al. . Pocket haematoma after cardiac electronic device implantation in patients receiving antiplatelet and anticoagulant treatment: a single-centre experience. Acta Cardiol 72: 47-52, 2017. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

