Identification of epilepsy-associated neuronal subtypes and gene expression underlying epileptogenesis
- PMID: 33028830
- PMCID: PMC7541486
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18752-7
Identification of epilepsy-associated neuronal subtypes and gene expression underlying epileptogenesis
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Identification of epilepsy-associated neuronal subtypes and gene expression underlying epileptogenesis.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 19;11(1):5988. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19869-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33214565 Free PMC article.
Abstract
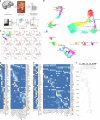
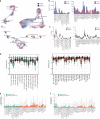
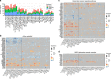
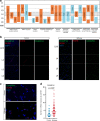
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders, yet its pathophysiology is poorly understood due to the high complexity of affected neuronal circuits. To identify dysfunctional neuronal subtypes underlying seizure activity in the human brain, we have performed single-nucleus transcriptomics analysis of >110,000 neuronal transcriptomes derived from temporal cortex samples of multiple temporal lobe epilepsy and non-epileptic subjects. We found that the largest transcriptomic changes occur in distinct neuronal subtypes from several families of principal neurons (L5-6_Fezf2 and L2-3_Cux2) and GABAergic interneurons (Sst and Pvalb), whereas other subtypes in the same families were less affected. Furthermore, the subtypes with the largest epilepsy-related transcriptomic changes may belong to the same circuit, since we observed coordinated transcriptomic shifts across these subtypes. Glutamate signaling exhibited one of the strongest dysregulations in epilepsy, highlighted by layer-wise transcriptional changes in multiple glutamate receptor genes and strong upregulation of genes coding for AMPA receptor auxiliary subunits. Overall, our data reveal a neuronal subtype-specific molecular phenotype of epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

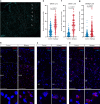
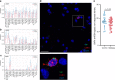
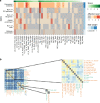
Comment in
-
Cells That "Fire Together, Wire Together", but Do They Transcribe Together in Epilepsy?Epilepsy Curr. 2021 Mar;21(2):124-125. doi: 10.1177/1535759721990042. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Epilepsy Curr. 2021. PMID: 33508978 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

