Iatrogenic left vertebral artery pseudoaneurysm treated with a covered stent
- PMID: 33029359
- PMCID: PMC7526994
- DOI: 10.1259/bjrcr.20190051
Iatrogenic left vertebral artery pseudoaneurysm treated with a covered stent
Abstract
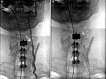
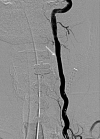
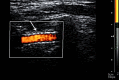
Vertebral artery pseudoaneurysm usually occurs after major trauma, but it can arise spontaneously after trivial injury. Clinical manifestations are often related to alterations in the posterior brain circulation. CT and angiography are usually the diagnostic methods of choice. We present a case of a pseudoaneurysm of the left vertebral artery caused by a lesion during a cervical spine surgery and treated with endovascular approach with a covered stent.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

