Transient Cardiac Dysfunction in Cerebrovascular Accidents
- PMID: 33029464
- PMCID: PMC7529496
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10185
Transient Cardiac Dysfunction in Cerebrovascular Accidents
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Transient Cardiac Dysfunction in Cerebrovascular Accidents.Cureus. 2021 Mar 5;13(3):r24. doi: 10.7759/cureus.r24. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33728231 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Acute cerebral injuries have been repeatedly correlated with sudden and different electrocardiogram (EKG) changes, such as cardiac arrhythmias, QT prolongation, and abnormal T-wave morphology. One rare phenomenon is "cerebral T-waves," which are T-waves observed in the context of stroke and described as transient, symmetric, and deeply inverted. Moreover, few studies linked acute cerebral injuries with transient cardiac dysfunction secondary to autonomic dysfunction. The classic cerebral T-waves are defined as a T-wave inversion of ≥5 mm depth in ≥4 contiguous precordial leads, and it is more commonly observed in the setting of acute ischemic stroke rather than hemorrhagic stroke. We present a patient who presented with acute pulmonary edema, T-wave inversions in the precordial leads, and left ventricular (LV) dysfunction initially suspicious for acute coronary syndrome (ACS). However, computer tomography of the brain performed on the third day of his hospital stay proved us wrong.
Keywords: acute cerebrovascular accidents; cerebral t waves; left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
Copyright © 2020, Elkhouly et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
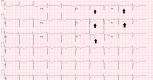


References
-
- Electrocardiographic T-wave changes underlying acute cardiac and cerebral events. Catanzaro JN, Meraj PM, Zheng S, Bloom G, Roethel M, Makaryus AN. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26:0. - PubMed
-
- Acute right middle cerebral artery occlusion resulting in acute systolic heart failure, cerebral T-waves, and QTc prolongation: a case report. Blech B, O'Carroll C. Neurologist. 2018;4:135–137. - PubMed
-
- Frequency of inverted electrocardiographic T waves (cerebral T waves) in patients with acute strokes and their relation to left ventricular wall motion abnormalities. Stone J, Mor-Avi V, Ardelt A, Lang RM. Am J Cardiol. 2018;121:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Cardiac effects of stimulation and block of the stellate ganglion. Rogers MC, Abildskov JA, Preston JB. Anesthesiology. 1973;39:525–533. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
