Management of Postpartum Hemorrhage With a Mini-Sponge Tamponade Device
- PMID: 33030862
- PMCID: PMC7575022
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004135
Management of Postpartum Hemorrhage With a Mini-Sponge Tamponade Device
Abstract
Background: Postpartum hemorrhage is a leading cause of maternal mortality globally. A tamponade agent that can be quickly and easily placed in a range of settings could advance the treatment of atonic hemorrhage.
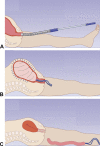
Method: We adapted a highly effective trauma dressing for use in postpartum hemorrhage. This mini-sponge tamponade device is comprised of two components: compressed mini-sponges contained within a strong mesh pouch and a tubular applicator. Compressed mini-sponges rapidly absorb blood, expand within seconds, and exert sustained pressure uniformly to bleeding sites. The sponges are deployed within a mesh pouch to facilitate simple vaginal removal.
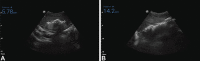
Experience: We successfully placed the mini-sponge device in nine patients experiencing postpartum hemorrhage after vaginal birth, with resolution of bleeding within 1 minute. The mean time to place the device was 62 seconds. Uterine fill was documented in all cases by ultrasound scan, and device placement was rated as "easy" to "very easy." Mini-sponges were left in place on average for 1 hour (0.5 hours-14 hours). Bleeding did not recur. There were no adverse events; all patients remained afebrile and did not require subsequent surgical intervention.
Conclusion: This study supports further evaluation of the mini-sponge device for the management of postpartum hemorrhage.
Funding: This study was funded by OBSTETRX, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
New Approaches to the Age-Old Problem of Uterine Atony.Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Nov;136(5):874-875. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004156. Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 33095541 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for the prevention and management of postpartum haemorrhage. World Health Organization: Geneva (Switzerland); 2012.
-
- Bakri YN, Amri A, Abdul Jabbar F. Tamponade-balloon for obstetrical bleeding. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2001;74:139–42. - PubMed
-
- Bakri YN. Uterine tamponade-drain for hemorrhage secondary to placenta previa-accreta. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 1992;37:302–3. - PubMed
-
- Dabelea V, Schultze PM, McDuffie RS., Jr Intrauterine balloon tamponade in the management of postpartum hemorrhage. Am J Perinatol 2007;24:359–64. - PubMed
-
- Vitthala S, Tsoumpou I, Anjum ZK, Aziz NA. Use of Bakri balloon in post-partum haemorrhage: a series of 15 cases. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2009;49:191–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

