TDP-43 Triggers Mitochondrial DNA Release via mPTP to Activate cGAS/STING in ALS
- PMID: 33031745
- PMCID: PMC7599077
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.020
TDP-43 Triggers Mitochondrial DNA Release via mPTP to Activate cGAS/STING in ALS
Abstract
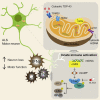
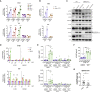
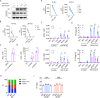
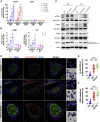
Cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 is a disease hallmark for many cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), associated with a neuroinflammatory cytokine profile related to upregulation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and type I interferon (IFN) pathways. Here we show that this inflammation is driven by the cytoplasmic DNA sensor cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP)-AMP synthase (cGAS) when TDP-43 invades mitochondria and releases DNA via the permeability transition pore. Pharmacologic inhibition or genetic deletion of cGAS and its downstream signaling partner STING prevents upregulation of NF-κB and type I IFN induced by TDP-43 in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived motor neurons and in TDP-43 mutant mice. Finally, we document elevated levels of the specific cGAS signaling metabolite cGAMP in spinal cord samples from patients, which may be a biomarker of mtDNA release and cGAS/STING activation in ALS. Our results identify mtDNA release and cGAS/STING activation as critical determinants of TDP-43-associated pathology and demonstrate the potential for targeting this pathway in ALS.
Keywords: ALS; IFN; NF-κB; STING; TDP-43; cGAMP; cGAS; mPTP; mitochondria; neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests S.L.M. declares consultancy with IFM Therapeutics and Quench Bio and received funding from GlaxoSmithKline. S.L.M. and C.-H.Y. are named inventors on International Patent Application No. PCT/AU2019051201. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

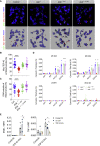


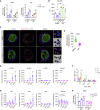

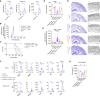

Comment in
-
TDP-43 Puts the STING in ALS.Trends Neurosci. 2021 Feb;44(2):81-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.12.001. Epub 2020 Dec 20. Trends Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33353765
-
TDP-43 triggers immune response via mitochondrial DNA release.Cell Res. 2021 Apr;31(4):379-380. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00461-x. Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33603118 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Activation of cGAS/STING pathway upon TDP-43-mediated mitochondrial injury may be involved in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis.Liver Int. 2021 Aug;41(8):1969-1971. doi: 10.1111/liv.14895. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Liver Int. 2021. PMID: 33830629 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arnold E.S., Ling S.C., Huelga S.C., Lagier-Tourenne C., Polymenidou M., Ditsworth D., Kordasiewicz H.B., McAlonis-Downes M., Platoshyn O., Parone P.A. ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:E736–E745. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker P.J., Masters S.L. Generation of Genetic Knockouts in Myeloid Cell Lines Using a Lentiviral CRISPR/Cas9 System. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018;1714:41–55. - PubMed
-
- Balka K.R., Louis C., Saunders T.L., Smith A.M., Calleja D.J., D’Silva D.B., Moghaddas F., Tailler M., Lawlor K.E., Zhan Y. TBK1 and IKKε Act Redundantly to Mediate STING-Induced NF-κB Responses in Myeloid Cells. Cell Rep. 2020;31:107492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

