Safety of Intravenous Heparin for Cardiac Surgery in Patients With Alpha-Gal Syndrome
- PMID: 33031779
- PMCID: PMC8019687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.07.050
Safety of Intravenous Heparin for Cardiac Surgery in Patients With Alpha-Gal Syndrome
Abstract
Background: Alpha-gal syndrome is a tick-acquired disease caused by immunoglobulin E (IgE) to the oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal), causing allergic reactions to meat and products sourced from nonprimate mammals. As heparin is porcine-derived, we hypothesized that patients with alpha-gal syndrome who received high-dose heparin for cardiac surgery would have increased risk of anaphylaxis.
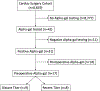
Methods: All cardiac surgery patients at an academic medical center from 2007 to 2019 were cross-referenced with research and clinical databases for the alpha-gal IgE blood test. Clinical data were obtained through the institutional Society of Thoracic Surgeons Adult Cardiac Database and chart review. Patients were stratified by development of an allergic reaction for univariate statistical analysis.
Results: Of the 8819 patients, 17 (0.19%) had a positive alpha-gal test before cardiac surgery. Of these 17 patients, 4 (24%) had a severe allergic reaction. The median alpha-gal titer was significantly higher in patients with a reaction (75 [interquartile range, 61-96] IU/mL vs 8 [interquartile range, 3-18] IU/mL; P = .006). There were no differences in median heparin loading dose, total dose, or maximum activated clotting time (all P > .05). In a subgroup of 8 patients with recent alpha-gal IgE level, 4 (50%) developed an allergic reaction.
Conclusions: Although alpha-gal is rare in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, there is up to a 50% risk of serious allergic reaction to heparin for cardiopulmonary bypass. Higher preoperative alpha-gal titers may confer a higher risk of severe allergic reaction. For patients with a clinical suspicion of alpha-gal syndrome, we recommend prescreening with IgE levels and premedicating before receiving high doses of intravenous heparin.
Copyright © 2021 The Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
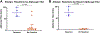

References
-
- Oriol R, Ye Y, Koren E, Cooper DK. Carbohydrate antigens of pig tissues reacting with human natural antibodies as potential targets for hyperacute vascular rejection in pig-to-man organ xenotransplantation. Transplantation 1993;56:1433–1442. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JM, Platts-Mills TA. The oligosaccharide galactose-α−1,3-galactose and the α-gal syndrome: Insights from an epitope that is causal in immunoglobulin e-mediated immediate and delayed anaphylaxis. EMJ Allergy Immunol 2018;3:89–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

