Heterogeneous mass distribution of the rubble-pile asteroid (101955) Bennu
- PMID: 33033036
- PMCID: PMC7544499
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc3350
Heterogeneous mass distribution of the rubble-pile asteroid (101955) Bennu
Abstract
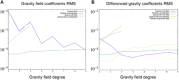
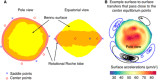
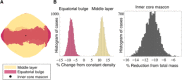
The gravity field of a small body provides insight into its internal mass distribution. We used two approaches to measure the gravity field of the rubble-pile asteroid (101955) Bennu: (i) tracking and modeling the spacecraft in orbit about the asteroid and (ii) tracking and modeling pebble-sized particles naturally ejected from Bennu's surface into sustained orbits. These approaches yield statistically consistent results up to degree and order 3, with the particle-based field being statistically significant up to degree and order 9. Comparisons with a constant-density shape model show that Bennu has a heterogeneous mass distribution. These deviations can be modeled with lower densities at Bennu's equatorial bulge and center. The lower-density equator is consistent with recent migration and redistribution of material. The lower-density center is consistent with a past period of rapid rotation, either from a previous Yarkovsky-O'Keefe-Radzievskii-Paddack cycle or arising during Bennu's accretion following the disruption of its parent body.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures



References
-
- Russell C. T., Raymond C. A., Coradini A., McSween H. Y., Zuber M. T., Nathues A., De Sanctis M. C., Jaumann R., Konopliv A. S., Preusker F., Asmar S. W., Park R. S., Gaskell R., Keller H. U., Mottola S., Roatsch T., Scully J. E. C., Smith D. E., Tricarico P., Toplis M. J., Christensen U. R., Feldman W. C., Lawrence D. J., McCoy T. J., Prettyman T. H., Reedy R. C., Sykes M. E., Titus T. N., Dawn at Vesta: Testing the protoplanetary paradigm. Science 336, 684–686 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Ermakov A. I., Zuber M. T., Smith D. E., Raymond C. A., Balmino G., Fu R. R., Ivanov B. A., Constraints on Vesta’s interior structure using gravity and shape models from the Dawn mission. Icarus 240, 146–160 (2014).
-
- Park R. S., Konopliv A. S., Bills B. G., Rambaux N., Castillo-Rogez J. C., Raymond C. A., Vaughan A. T., Ermakov A. I., Zuber M. T., Fu R. R., Toplis M. J., Russell C. T., Nathues A., Preusker F., A partially differentiated interior for (1) Ceres deduced from its gravity field and shape. Nature 537, 515–517 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Ermakov A. I., Fu R. R., Castillo-Rogez J. C., Raymond C. A., Park R. S., Preusker F., Russell C. T., Smith D. E., Zuber M. T., Constraints on Ceres’ internal structure and evolution from its shape and gravity measured by the Dawn spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 122, 2267–2293 (2017).
-
- Konopliv A. S., Park R. S., Vaughan A. T., Bills B. G., Asmar S. W., Ermakov A. I., Rambaux N., Raymond C. A., Castillo-Rogez J. C., Russell C. T., Smith D. E., Zuber M. T., The Ceres gravity field, spin pole, rotation period and orbit from the Dawn radiometric tracking and optical data. Icarus 299, 411–429 (2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

