Plasmid diversity among genetically related Klebsiella pneumoniae blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 isolates collected in the Dutch national surveillance
- PMID: 33033293
- PMCID: PMC7546619
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73440-2
Plasmid diversity among genetically related Klebsiella pneumoniae blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 isolates collected in the Dutch national surveillance
Abstract
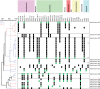
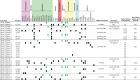
Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae emerged as a nosocomial pathogen causing morbidity and mortality in patients. For infection prevention it is important to track the spread of K. pneumoniae and its plasmids between patients. Therefore, the major aim was to recapitulate the contents and diversity of the plasmids of genetically related K. pneumoniae strains harboring the beta-lactamase gene blaKPC-2 or blaKPC-3 to determine their dissemination in the Netherlands and the former Dutch Caribbean islands from 2014 to 2019. Next-generation sequencing was combined with long-read third-generation sequencing to reconstruct 22 plasmids. wgMLST revealed five genetic clusters comprised of K. pneumoniae blaKPC-2 isolates and four clusters consisted of blaKPC-3 isolates. KpnCluster-019 blaKPC-2 isolates were found both in the Netherlands and the Caribbean islands, while blaKPC-3 cluster isolates only in the Netherlands. Each K. pneumoniae blaKPC-2 or blaKPC-3 cluster was characterized by a distinct resistome and plasmidome. However, the large and medium plasmids contained a variety of antibiotic resistance genes, conjugation machinery, cation transport systems, transposons, toxin/antitoxins, insertion sequences and prophage-related elements. The small plasmids carried genes implicated in virulence. Thus, implementing long-read plasmid sequencing analysis for K. pneumoniae surveillance provided important insights in the transmission of a KpnCluster-019 blaKPC-2 strain between the Netherlands and the Caribbean.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

