The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 33033392
- PMCID: PMC7542092
- DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00360-x
The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
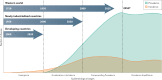
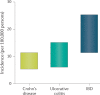
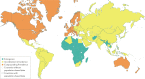
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a global disease; its evolution can be stratified into four epidemiological stages: Emergence, Acceleration in Incidence, Compounding Prevalence and Prevalence Equilibrium. In 2020, developing countries are in the Emergence stage, newly industrialized countries are in the Acceleration in Incidence stage, and Western regions are in the Compounding Prevalence stage. Western regions will eventually transition to the Prevalence Equilibrium stage, in which the accelerating prevalence levels off as the IBD population ages and possibly as a result of an unexpected rise in mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic. Mitigating the global burden of IBD will require concerted efforts in disease prevention and health-care delivery innovations that respond to changing demographics of the global IBD population. In this Perspective, we summarize the global epidemiology of IBD and use these data to stratify disease evolution into four epidemiological stages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

