MiR-135-5p inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting SMAD3 in breast cancer
- PMID: 33033523
- PMCID: PMC7532519
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.47083
MiR-135-5p inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting SMAD3 in breast cancer
Abstract
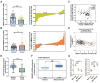
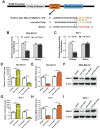
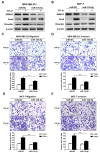
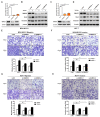
Breast cancer (BC) is the most frequently diagnosed malignant tumors and the leading cause of death due to cancer in women around the world. A growing body of studies have documented that microRNA (miR)-135-5p is associated with the development and progression of BC. Considering that sekelsky mothers against dpp3 (SMAD3) plays a crucial role in transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/SMAD pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process, it is critical to elucidate the crosstalk and underlying regulatory mechanisms between miR-135-5p and SMAD3 in controlling TGF-β-mediated EMT in BC metastasis. Our results revealed a reciprocal expression pattern between miR-135-5p and SMAD3 mRNA in BC tissues and cell lines. Moreover, miR-135-5p was decreased in BC tissues compared to adjacent breast tissues; more interesting, miR-135-5p mRNA levels (Tumor/Normal, T/N) was further decreased in BC patients with lymph node metastasis, while SMAD3 mRNA levels were increased. Gain- and loss-of-function assays indicated that overexpression of miR-135-5p inhibited TGF-β-mediated EMT and BC metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, knockdown of SMAD3 produced a consistent phenotype of miR-135-5p overexpression in breast cancer cells. Mechanistically, SMAD3, a pivotal transcriptional modulator of TGF-β/SMAD pathway, for the first time, was analyzed and identified as a target gene of miR-135-5p by bioinformatic algorithms and dual-luciferase reporter assays. Taken together, we clarified that miR-135-5p suppressed TGF-β-mediated EMT and BC metastasis by negatively regulating SMAD3 and TGF-β/SMAD signaling. Our findings supported that miR-135-5p may serve as a tumor suppressor, and be a valuable diagnostic biomarker for the treatment of BC.
Keywords: SMAD3; breast cancer; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; metastasis.; microRNA-135-5p.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of non-small cell lung cancer migration and invasion by hsa-miR-486-5p via the TGF-β/SMAD2 signaling pathway.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 15;10(24):6014-6024. doi: 10.7150/jca.35017. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31762811 Free PMC article.
-
Linc00511 Knockdown Inhibited TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Bronchial Epithelial Cells by Targeting miR-16-5p/Smad3.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2023 May;37(3):313-323. doi: 10.1177/19458924221144853. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2023. PMID: 36594176
-
miR-217-5p suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the NF-κB signaling pathway in breast cancer via targeting of metadherin.Oncol Lett. 2022 May;23(5):162. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13282. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35399330 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNA-204 in Regulating the Hallmarks of Breast Cancer: An Update.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 10;16(16):2814. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162814. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-361: A Multifaceted Player Regulating Tumor Aggressiveness and Tumor Microenvironment Formation.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 7;11(8):1130. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081130. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31394811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-22-3p/PGC1β Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Tumorigenesis via PPARγ.PPAR Res. 2021 Mar 12;2021:6661828. doi: 10.1155/2021/6661828. eCollection 2021. PPAR Res. 2021. PMID: 33777130 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-135-5p Alleviates Bone Cancer Pain by Regulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Spinal Cord through JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Oct;58(10):4802-4815. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02458-y. Epub 2021 Jun 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34176097
-
Integrated study of miR-215 promoting breast cancer cell apoptosis by targeting RAD54B.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Apr;25(7):3327-3338. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16402. Epub 2021 Feb 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33635591 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a basement membrane-related genes signature with immune correlation in bladder urothelial carcinoma and verification in vitro.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 23;23(1):1021. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11340-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37872487 Free PMC article.
-
SMAD Proteins in TGF-β Signalling Pathway in Cancer: Regulatory Mechanisms and Clinical Applications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 26;13(17):2769. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13172769. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37685308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Pineros M. et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. International journal of cancer. 2019;144:1941–1953. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2018;68:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–695. - PubMed
-
- Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331:1559–1564. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

