Comprehensive review of hepatotoxicity associated with traditional Indian Ayurvedic herbs
- PMID: 33033566
- PMCID: PMC7522561
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i9.574
Comprehensive review of hepatotoxicity associated with traditional Indian Ayurvedic herbs
Abstract
With growing antipathy toward conventional prescription drugs due to the fear of adverse events, the general and patient populations have been increasingly using complementary and alternative medications (CAMs) for managing acute and chronic diseases. The general misconception is that natural herbal-based preparations are devoid of toxicity, and hence short- and long-term use remain justified among people as well as the CAM practitioners who prescribe these medicines. In this regard, Ayurvedic herbal medications have become one of the most utilized in the East, specifically the Indian sub-continent, with increasing use in the West. Recent well-performed observational studies have confirmed the hepatotoxic potential of Ayurvedic drugs. Toxicity stems from direct effects or from indirect effects through herbal metabolites, unknown herb-herb and herb-drug interactions, adulteration of Ayurvedic drugs with other prescription medicines, and contamination due to poor manufacturing practices. In this exhaustive review, we present details on their hepatotoxic potential, discuss the mechanisms, clinical presentation, liver histology and patient outcomes of certain commonly used Ayurvedic herbs which will serve as a knowledge bank for physicians caring for liver disease patients, to support early identification and treatment of those who present with CAM-induced liver injury.
Keywords: AYUSH system; Ayurveda; Chronic liver disease; Complementary and alternative medicines; Drug induced liver injury; Herb induced liver injury.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
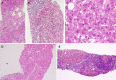
Figures



Similar articles
-
A comprehensive review on the hepatotoxicity of herbs used in the Indian (Ayush) systems of alternative medicine.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Apr 19;103(16):e37903. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037903. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38640296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scientific basis for the use of Indian ayurvedic medicinal plants in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: ashwagandha.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010 Sep 1;10(3):238-46. doi: 10.2174/1871524911006030238. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20528765 Review.
-
Complementary and alternative medicine use among cancer patients in Palestine with special reference to safety-related concerns.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jul 1;187:104-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.038. Epub 2016 Apr 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27125594
-
Herb-Drug Interactions and Hepatotoxicity.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(4):275-282. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190325141422. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 30914020 Review.
-
Herbal hepatotoxicity: current status, examples, and challenges.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015;11(10):1551-65. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2015.1064110. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26149408 Review.
Cited by
-
Curcuma longa Hepatotoxicity: A Baseless Accusation. Cases Assessed for Causality Using RUCAM Method.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 29;12:780330. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.780330. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34776989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) and Its Effects on Well-Being-A Review.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 27;17(13):2143. doi: 10.3390/nu17132143. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40647248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective role of resveratrol against VCM-induced hepatotoxicity in male wistar rats.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 7;14:1130670. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1130670. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36825158 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Withania somnifera on Cortisol Levels in Stressed Human Subjects: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 5;15(24):5015. doi: 10.3390/nu15245015. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38140274 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury: an update.Hepatol Int. 2024 Apr;18(2):384-419. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10633-7. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Hepatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38402364
References
-
- Udayakumar N, Subramaniam K, Umashankar L, Verghese J, Jayanthi V. Predictors of mortality in hepatic encephalopathy in acute and chronic liver disease: a preliminary observation. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;41:922–926. - PubMed
-
- Devarbhavi H, Choudhury AK, Sharma MK, Maiwall R, Al Mahtab M, Rahman S, Chawla YK, Dhiman RK, Duseja A, Taneja S, Ning Q, Jia JD, Duan Z, Yu C, Eapen CE, Goel A, Tan SS, Hamid SS, Butt AS, Jafri W, Kim DJ, Hu J, Sood A, Midha V, Shukla A, Ghazinian H, Sahu MK, Treeprasertsuk S, Lee GH, Lim SG, Lesmana LA, Lesmana CR, Shah S, Kalal C, Abbas Z, Sollano JD, Prasad VGM, Payawal DA, Dokmeci AK, Rao PN, Shrestha A, Lau GK, Yuen MF, Saraswat VA, Shiha G, Yokosuka O, Kedarisetty CK, Jain P, Bhatia P, Sarin SK APASL ACLF working party. Drug-Induced Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in Asian Patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114:929–937. - PubMed
-
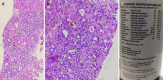
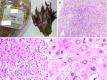
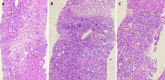
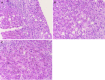
- Philips CA, Paramaguru R, Joy AK, Antony KL, Augustine P. Clinical outcomes, histopathological patterns, and chemical analysis of Ayurveda and herbal medicine associated with severe liver injury-A single-center experience from southern India. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018;37:9–17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

