Effect of risk messages on risk appraisals, attitudes, ambivalence, and willingness to smoke hookah in young adults
- PMID: 33033657
- PMCID: PMC7540838
- DOI: 10.1080/21642850.2020.1730844
Effect of risk messages on risk appraisals, attitudes, ambivalence, and willingness to smoke hookah in young adults
Abstract
Objective: We examined effects of hookah tobacco risk messages on risk appraisals, attitudes towards hookah, ambivalence about hookah use, and willingness to smoke in young adults aged 18-30 years (n = 234).
Design: In an online experiment, participants completed preexposure measures and were randomized to hookah tobacco risk messages or to a no message control condition.
Main outcome measures: Risk appraisals, attitudes, ambivalence, and willingness to smoke hookah.
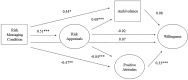
Results: Those who viewed risk messages reported greater risk appraisals (M 4.50, SD 1.17 vs. M 3.87, SD 1.16, p < .001), less positive attitudes (M -0.56, SD 1.24, vs. M 0.39, SD 1.35, p < .001), greater ambivalence (M 3.86, SD 1.26, vs. M 3.08, SD 1.32, p < .001), and less willingness to smoke than controls (M 4.48, SD 1.27, vs. M 4.85, SD 1.37, p = .034). Structural equation modeling demonstrated messages reduced willingness to smoke by evoking less positive attitudes (b = -0.15, 95% CI -0.32, -0.05) and by the effect of heightened risk appraisals on less positive attitudes (b = -0.14, 95% CI -0.30, -0.07).
Conclusions: Honing messages and understanding their mechanisms of action are necessary to produce more effective interventions to address hookah and other tobacco use in young adults.
Keywords: Young adults; ambivalence; attitude; risk communication; tobacco.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Akl, E. A., Ward, K. D., Bteddini, D., Khaliel, R., Alexander, A. C., Lotfi, T., … Afifi, R. A. (2015). The allure of the waterpipe: A narrative review of factors affecting the epidemic rise in waterpipe smoking among young persons globally. Tobacco Control, 24(Suppl 1), i13–i21. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2014-051906 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown, T. A. (2015). Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources