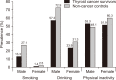Factors Associated with Health Behaviors in Thyroid Cancer Survivors
- PMID: 33033711
- PMCID: PMC7523035
- DOI: 10.15430/JCP.2020.25.3.173
Factors Associated with Health Behaviors in Thyroid Cancer Survivors
Abstract
In this study, we compared health behaviors, including current smoking, drinking, and physical inactivity, in thyroid cancer survivors and non-cancer controls and investigated the factors associated with unhealthy behaviors among survivors. Baseline data from the Health Examinees study, collected from 2004 to 2013, were used. Thyroid cancer survivors (n = 942), defined as those who had received a clinical diagnosis of thyroid cancer, and 9,420 matched non-cancer controls without past history of any cancer were included in the analysis. The prevalence of smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity in thyroid cancer survivors were 2.3%, 26.6%, and 52.0%, respectively, with adjusted OR (aOR) and 95% CI between survivors and non-cancer controls of 0.35 (95% CI = 0.08-1.56), 0.46 (95% CI = 0.29-0.74), and 0.65 (95% CI = 0.44-0.96). The prevalence of unhealthy behaviors was higher among male thyroid cancer survivors than female thyroid cancer survivors. In thyroid cancer survivors, those who smoked were more likely to drink (aOR = 4.55 [95% CI = 1.61-12.85]) and those who were physically inactive were less likely to drink (aOR = 0.58 [95% CI = 0.42-0.82]). Current drinking and physical inactivity contributed to a higher likelihood of smoking (aOR = 4.31 [95% CI = 1.35-13.73] and 6.34 [95% CI = 1.65-24.34]). Thyroid cancer survivors had better health behaviors than the non-cancer controls. However, some survivors still had unhealthy lifestyles, especially displaying a clustering of unhealthy behaviors. Thus, health behavior promotion through medical intervention is important for thyroid cancer survivors.
Keywords: Cancer survivors; Health behavior; Thyroid neoplasms.
Copyright © 2020 Korean Society of Cancer Prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Nickel B, Tan T, Cvejic E, Baade P, McLeod DSA, Pandeya N, et al. Health-related quality of life after diagnosis and treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer and association with type of surgical treatment. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;145:231–8. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2018.3870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous