Real-World Evidence to Contextualize Clinical Trial Results and Inform Regulatory Decisions: Tofacitinib Modified-Release Once-Daily vs Immediate-Release Twice-Daily for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 33034006
- PMCID: PMC7854470
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-020-01501-z
Real-World Evidence to Contextualize Clinical Trial Results and Inform Regulatory Decisions: Tofacitinib Modified-Release Once-Daily vs Immediate-Release Twice-Daily for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To provide additional clinical evidence in regulatory submissions for a modified-release (MR) once-daily (QD) tofacitinib formulation, we compared real-world adherence and effectiveness between patients initiating the MR QD formulation and patients initiating an immediate-release (IR) twice-daily (BID) formulation.
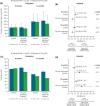
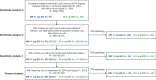
Methods: Two noninterventional cohort studies were conducted. First, adherence and two effectiveness proxies were compared between patients with RA who newly initiated tofacitinib MR 11 mg QD or IR 5 mg BID in the IBM® MarketScan® Commercial and Medicare Supplemental US insurance claims databases (March 2016-October 2018). Second, using data collected in the Corrona US RA Registry (February 2016-August 2019), two Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI)-based measures of effectiveness were compared between tofacitinib MR 11 mg QD and IR 5 mg BID, and against noninferiority criteria derived from placebo-controlled clinical trials of the tofacitinib IR formulation. Multiple sensitivity analyses of the registry data were conducted to reassure regulators of consistent results across different assumptions.
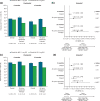
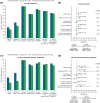
Results: In each study, approximately two-thirds of patients initiated the MR formulation. In the claims database study, improved adherence and at least comparable effectiveness were observed with tofacitinib MR vs IR over 12 months, particularly in patients without prior advanced therapy. In the registry study, the noninferiority of tofacitinib MR vs IR was demonstrated for both CDAI outcomes at ~6 months; this finding was robust across multiple sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate the value of real-world evidence from complementary data sources in understanding the impact of medication adherence with a QD formulation in clinical practice. These analyses were suitable for regulatory consideration as an important component of evidence for the comparability of tofacitinib MR 11 mg QD vs IR 5 mg BID in patients with RA.
Trial registration: Claims database study: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT04018001, retrospectively registered July 12, 2019. Corrona US RA Registry study: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT04267380, retrospectively registered February 12, 2020.
Keywords: Claims analysis; Clinical effectiveness; Drug approval process; Registry; Rheumatoid arthritis; Rheumatology; Tofacitinib.
Figures

References
-
- Silverman B. A baker’s dozen of US FDA efficacy approvals using real world evidence. 2018. https://pink.pharmaintelligence.informa.com/PS123648/A-Bakers-Dozen-Of-U.... Accessed 27 Feb 2020.
-
- European Medicines Agency. Adaptive pathways. 2016. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/research-development/adapt.... Accessed 5 Feb 2020.
-
- European Medicines Agency. HMA–EMA Joint Big Data Taskforce—summary report. 2019. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/minutes/hma/ema-joint-task-force-.... Accessed 5 Feb 2020.
-
- Health Canada. Optimizing the use of real world evidence to inform regulatory decision-making. 2019. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/dr.... Accessed 5 Feb 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

