Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33034020
- PMCID: PMC7543961
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-020-01531-3
Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Purpose: SARS-CoV-2 is a recently emerged ß-coronavirus. Here we present the current knowledge on its epidemiologic features.
Methods: Non-systematic review.
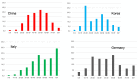
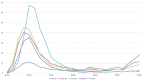
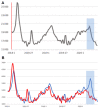
Results: SARS-CoV-2 replicates in the upper and lower respiratory tract. It is mainly transmitted by droplets and aerosols from asymptomatic and symptomatic infected subjects. The consensus estimate for the basis reproduction number (R0) is between 2 and 3, and the median incubation period is 5.7 (range 2-14) days. Similar to SARS and MERS, superspreading events have been reported, the dispersion parameter (kappa) is estimated at 0.1. Most infections are uncomplicated, and 5-10% of patients are hospitalized, mainly due to pneumonia with severe inflammation. Complications are respiratory and multiorgan failure; risk factors for complicated disease are higher age, hypertension, diabetes, chronic cardiovascular, chronic pulmonary disease and immunodeficiency. Nosocomial and infections in medical personnel have been reported. Drastic reductions of social contacts have been implemented in many countries with outbreaks of SARS-CoV-2, leading to rapid reductions. Most interventions have used bundles, but which of the measures have been more or less effective is still unknown. The current estimate for the infection's fatality rate is 0.5-1%. Using current models of age-dependent infection fatality rates, upper and lower limits for the attack rate in Germany can be estimated between 0.4 and 1.6%, lower than in most European countries.
Conclusions: Despite a rapid worldwide spread, attack rates have been low in most regions, demonstrating the efficacy of control measures.
Keywords: Basic reproduction number; COVID-19; Epidemiology; Incubation period; Infection fatality risk; Mortality; Pandemic; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
None reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19].Gastroenterologe. 2020;15(6):443-451. doi: 10.1007/s11377-020-00479-y. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Gastroenterologe. 2020. PMID: 33144889 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
[Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19].Internist (Berl). 2020 Aug;61(8):782-788. doi: 10.1007/s00108-020-00834-9. Internist (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32548652 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
[SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19-epidemiology and prevention].Nephrologe. 2021;16(1):3-9. doi: 10.1007/s11560-020-00472-0. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Nephrologe. 2021. PMID: 33343742 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Household secondary attack rate of COVID-19 and associated determinants in Guangzhou, China: a retrospective cohort study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;20(10):1141-1150. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30471-0. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32562601 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring Basic Reproduction Number to Assess Effects of Nonpharmaceutical Interventions on Nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 Transmission.Emerg Infect Dis. 2022 Jul;28(7):1345-1354. doi: 10.3201/eid2807.212339. Epub 2022 May 17. Emerg Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35580960 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunological Studies to Understand Hybrid/Recombinant Variants of SARS-CoV-2.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;11(1):45. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11010045. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36679891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bronchial epithelia from adults and children: SARS-CoV-2 spread via syncytia formation and type III interferon infectivity restriction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 12;119(28):e2202370119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202370119. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35749382 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Bogotá, Colombia: Results From a Large Epidemiological Surveillance Study.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2021 Oct;2:100048. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2021.100048. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2021. PMID: 34458886 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Psychological Impacts on Healthcare Providers during COVID-19 Pandemic in Asia.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 30;18(17):9157. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18179157. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental predictors of SARS-CoV-2 infection incidence in Catalonia (northwestern Mediterranean).Front Public Health. 2024 Dec 5;12:1430902. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1430902. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39703486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) Situation Report, 25.08.2020. Geneva. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed 25.08.2020.
-
- RKI. TäglicherLagebericht des RKI zur Coronavirus-Krankheit-2019 (COVID-19) 25.08.2020 – AKTUALISIERTER STAND FÜR DEUTSCHLAND. Berlin: Robert-Koch-Institut2020 25.08.2020.
-
- 3–5
-
- WHO. Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Geneva: WHO2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

