Neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2 spike in COVID-19 patients, health care workers, and convalescent plasma donors
- PMID: 33035201
- PMCID: PMC7710271
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.143213
Neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2 spike in COVID-19 patients, health care workers, and convalescent plasma donors
Abstract
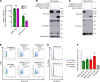
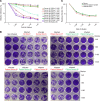
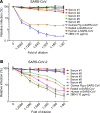
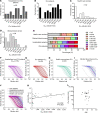
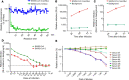
Rapid and specific antibody testing is crucial for improved understanding, control, and treatment of COVID-19 pathogenesis. Herein, we describe and apply a rapid, sensitive, and accurate virus neutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The assay is based on an HIV-1 lentiviral vector that contains a secreted intron Gaussia luciferase (Gluc) or secreted nano-luciferase reporter cassette, pseudotyped with the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) glycoprotein, and is validated with a plaque-reduction assay using an authentic, infectious SARS-CoV-2 strain. The assay was used to evaluate SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in serum from individuals with a broad range of COVID-19 symptoms; patients included those in the intensive care unit (ICU), health care workers (HCWs), and convalescent plasma donors. The highest neutralizing antibody titers were observed among ICU patients, followed by general hospitalized patients, HCWs, and convalescent plasma donors. Our study highlights a wide phenotypic variation in human antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 and demonstrates the efficacy of a potentially novel lentivirus pseudotype assay for high-throughput serological surveys of neutralizing antibody titers in large cohorts.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cellular immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Update of
-
Neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2 spike in COVID-19 patients, health care workers and convalescent plasma donors: a cohort study using a rapid and sensitive high-throughput neutralization assay.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 4:2020.08.02.20166819. doi: 10.1101/2020.08.02.20166819. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: JCI Insight. 2020 Nov 19;5(22):143213. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.143213. PMID: 32793931 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- [No authors listed]. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Situation Report. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... Accessed October 15, 2020.
-
- doi: 10.1101/2020.04.30.2008567. Hachim A, et al. Beyond the Spike: identification of viral targets of the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients. medRxiv. Published May 22, 2020. Accessed October 15, 2020. - DOI
-
- Luchsinger LL, et al. Serological Assays Estimate Highly Variable SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Activity in Recovered COVID19 Patients [published ahead of print September 11, 2020]. J Clin Microbiol. https://doi.org 10.1128/JCM.02005-20. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI121212/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097376/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD095881/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI106697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI151230/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL096376/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098174/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130110/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA260582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI146690/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150473/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI134035/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI112381/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

