Single Residue Variation in Skeletal Muscle Myosin Enables Direct and Selective Drug Targeting for Spasticity and Muscle Stiffness
- PMID: 33035452
- PMCID: PMC7596007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.050
Single Residue Variation in Skeletal Muscle Myosin Enables Direct and Selective Drug Targeting for Spasticity and Muscle Stiffness
Abstract
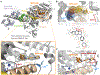
Muscle spasticity after nervous system injuries and painful low back spasm affect more than 10% of global population. Current medications are of limited efficacy and cause neurological and cardiovascular side effects because they target upstream regulators of muscle contraction. Direct myosin inhibition could provide optimal muscle relaxation; however, targeting skeletal myosin is particularly challenging because of its similarity to the cardiac isoform. We identified a key residue difference between these myosin isoforms, located in the communication center of the functional regions, which allowed us to design a selective inhibitor, MPH-220. Mutagenic analysis and the atomic structure of MPH-220-bound skeletal muscle myosin confirmed the mechanism of specificity. Targeting skeletal muscle myosin by MPH-220 enabled muscle relaxation, in human and model systems, without cardiovascular side effects and improved spastic gait disorders after brain injury in a disease model. MPH-220 provides a potential nervous-system-independent option to treat spasticity and muscle stiffness.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; blebbistatin; crystallography; deep learning; force; motor protein; musculoskeletal disorder; sarcomere; stroke; unmet medical need.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare the following competing interests: employment, A.M.-C. and M.G. are owners of Motorpharma, Ltd. and A.Á.R. and M.G. are part-time employed by Motorpharma, Ltd.; related patents, PCT/EP2017/051829, WO/2017/129782, HU1800129A2, PCT/HU2019/050017, WO/2019/202346A2, and WO/2019/202346A3; J.A.S. is a cofounder and member of the scientific advisory boards of Cytokinetics and MyoKardia, biotechnology companies developing small molecules that target the sarcomere for the treatment of various muscle diseases; K.M.R. is on the scientific advisory board at MyoKardia; and J.A.S., D.V.T., and K.M.R. are cofounders of Kainomyx Inc., a biotechnology company focused on developing small molecules to target tropical diseases.
Figures
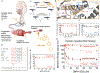


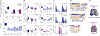
References
-
- Allingham JS, Smith R, and Rayment I (2005). The structural basis of blebbistatin inhibition and specificity for myosin II. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12, 378–379. - PubMed
-
- Berman H, Henrick K, and Nakamura H (2003). Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat Struct Biol 10, 980. - PubMed
-
- Bjornsdottir A, Gudmundsson G, Blondal H, and Olafsson E (2013). Incidence and prevalence of multiple system atrophy: a nationwide study in Iceland. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry 84, 136–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

