SFPH proteins as therapeutic targets for a myriad of diseases
- PMID: 33035678
- PMCID: PMC7536521
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127600
SFPH proteins as therapeutic targets for a myriad of diseases
Abstract
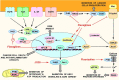
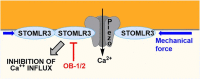
The stomatin/prohibitin/flotillin/HflK/HflC (SPFH) domain is present in an evolutionarily conserved family of proteins that regulate a myriad of signaling pathways in archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes. The most studied SPFH proteins, prohibitins, have already been targeted by different families of small molecules to induce anticancer, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antiosteoporotic activities. Ligands of other SPFH proteins have also been identified and shown to act as anesthetics, anti-allodynia, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory agents. These findings indicate that modulators of human or bacterial SPFH proteins can be developed to treat a wide variety of human disorders.
Keywords: Allodynia; Anesthesia; Cancer; Drug discovery; Infectious diseases; Lipid rafts; Scaffold proteins.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Browman D.T., Hoegg M.B., Robbins S.M. The SPFH domain-containing proteins: more than lipid raft markers. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17(8):394–402. - PubMed
-
- Danek M., Valentova O., Martinec J. Flotillins, Erlins, and HIRs: From Animal Base Camp to Plant New Horizons. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2016;35(4):191–214.
-
- Morrow I.C., Parton R.G. Flotillins and the PHB domain protein family: Rafts, worms and anesthetics. Traffic. 2005;6(9):725–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

