Relation of D-dimer levels of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 33035824
- PMCID: PMC7528836
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.09.035
Relation of D-dimer levels of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background and aims: Diabetes is a frequent comorbidity in patients with Severe COVID-19 infection associated with a worse prognosis. Hypercoagulability with elevation in D-dimer levels has been demonstrated in patients with COVID-19. This study aims to study D-dimer levels in people with diabetes compared to those without diabetes among patients with COVID-19 infection.
Methods: In this observational study 98 moderate and severely ill patients with COVID-19 infection were included at a dedicated COVID hospital. The study group was divided into patients with diabetes and without diabetes. Peak D-dimer was measured in both the groups and compared using appropriate statistical tests.
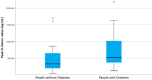
Results: In our study peak D-dimer levels were 1509 ± 2420 ng/mL (Mean ± SD) in people with diabetes and 515 ± 624 ng/mL (Mean ± SD) in patients without diabetes. Patients with diabetes had higher D-dimer levels which were statistically significant.
Conclusions: This study shows COVID-19 patients with diabetes had significantly higher D-dimer levels. Therefore, it is possible that COVID-19 infection with diabetes is more likely to cause hypercoagulable state with a worse prognosis. However clinical implications of these findings will need to be seen in further studies.
Keywords: COVID-19; D-dimer; Diabetes.
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Coronavirus COVID-19 (2019-nCoV) https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594... [Internet]. [cited 2020 Sep 13]. Available from:
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA, J Am Med Assoc. 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical