Developments in integrating nucleic acid isothermal amplification and detection systems for point-of-care diagnostics
- PMID: 33035900
- PMCID: PMC7529604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112674
Developments in integrating nucleic acid isothermal amplification and detection systems for point-of-care diagnostics
Abstract
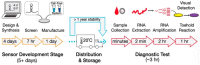
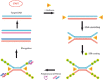
Early disease detection through point-of-care (POC) testing is vital for quickly treating patients and preventing the spread of harmful pathogens. Disease diagnosis is generally accomplished using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) to amplify nucleic acids in patient samples, permitting detection even at low target concentrations. However, qPCR requires expensive equipment, trained personnel, and significant time. These resources are not available in POC settings, driving researchers to instead utilize isothermal amplification, conducted at a single temperature, as an alternative. Common isothermal amplification methods include loop-mediated isothermal amplification, recombinase polymerase amplification, rolling circle amplification, nucleic acid sequence-based amplification, and helicase-dependent amplification. There has been a growing interest in combining such amplification methods with POC detection methods to enable the development of diagnostic tests that are well suited for resource-limited settings as well as developed countries performing mass screenings. Exciting developments have been made in the integration of these two research areas due to the significant impact that such approaches can have on healthcare. This review will primarily focus on advances made by North American research groups between 2015 and June 2020, and will emphasize integrated approaches that reduce user steps, reliance on expensive equipment, and the system's time-to-result.
Keywords: Isothermal amplification; LAMP; Nucleic acids; Point-of-care detection; RPA; Review.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






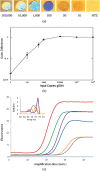
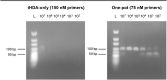
Similar articles
-
Strategies for Engineering Affordable Technologies for Point-of-Care Diagnostics of Infectious Diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Oct 19;54(20):3772-3779. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00434. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34612619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAATs): COVID-19 point-of-care diagnostics as an example.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Jun 15;206:114109. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114109. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35245867 Review.
-
Current Trends in RNA Virus Detection via Nucleic Acid Isothermal Amplification-Based Platforms.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 11;14(2):97. doi: 10.3390/bios14020097. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Point-of-Care Diagnostics Using Self-heating Elements from Smart Food Packaging: Moving Towards Instrument-Free Nucleic Acid-Based Detection.Mol Diagn Ther. 2025 Jan;29(1):67-80. doi: 10.1007/s40291-024-00753-7. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Mol Diagn Ther. 2025. PMID: 39550729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isothermal Amplification Techniques: An Emerging Tool for On-Site Detection of Phytopathogens in Field Conditions.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2943:47-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4642-7_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40580284 Review.
Cited by
-
Positive feedback drives a secondary nonlinear product burst during a biphasic DNA amplification reaction.Analyst. 2022 Oct 10;147(20):4450-4461. doi: 10.1039/d2an01067d. Analyst. 2022. PMID: 36164933 Free PMC article.
-
Thin-Film-Based Multifunctional System for Optical Detection and Thermal Treatment of Biological Samples.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 4;12(11):969. doi: 10.3390/bios12110969. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354478 Free PMC article.
-
A high-specificity flap probe-based isothermal nucleic acid amplification method based on recombinant FEN1-Bst DNA polymerase.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Nov 15;192:113503. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113503. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 34303138 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Detection of Clostridium tetani by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Using an Exo Probe.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 28;32(1):91-98. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2109.09022. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34818665 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolates by isothermal amplification and association of their virulence genes and phylogroups with extraintestinal infection.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 25;13(1):12022. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39228-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37491387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali M.M., Li F., Zhang Z., Zhang K., Kang D., Ankrum J.A., Le X.C., Zhao W. Rolling circle amplification: a versatile tool for chemical biology, materials science and medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014;43:3324–3341. - PubMed
-
- Ao W., Jenison R. Detection of rpoB gene mutations using helicase-dependent amplification. In: Kolpashchikov D.M., Gerasimova Y.V., editors. Nucleic Acid Detection: Methods and Protocols. Humana Press; New Jersey: 2013. pp. 89–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

