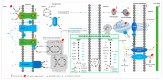
Figure 1
Plant abiotic stress perception and response, concerning different cell compartments/organelles, and the terpenoid biosynthesis pathway. Stress perception is sensed anywhere in the cell where there is a perturbation of biomolecules and metabolic reactions in various cellular compartments/organelles. Ca2+ signaling is initiated through [Ca2+]cyt changes due to the influx of Ca2+ or its release from intracellular calcium stores. Changes in [Ca2+]cyt are sensed by various calcium-binding proteins (e.g., calmodulin, CBL), and signals are relayed to the nucleus through the SOS pathway. Ca2+ also activates other pathways such as ABA signaling. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in the apoplast is initiated in response to Ca2+ and ABA signaling, and, together, Ca2+/ROS signals are automatically propagated to initiate an SAA or distal response. Mechano-sensitive channels through the CWI pathway may also play a role in sensing cellular stress and initiating a signal transduction cascade. ROS during stress is generated at various hotspots, particularly in metabolically active organelles, i.e., chloroplast, mitochondria, peroxisomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum. When ROS production exceeds the quenching capacity of the cell or cellular organelles, retrograde signaling is initiated either through ROS or through ROS-activated/dependent signaling pathways. ROS signals from different organelles may be integrated and fine-tuned through the ER–MCS. To prevent photoinhibition in the chloroplast, particularly that of PSII, CEF, Mehler peroxidase reaction, and photorespiration may relieve the system of the excess of reducing equivalents, while antioxidant defense systems such as the ascorbate–glutathione cycle may alleviate oxidative stress by quenching ROS. PSI/II, photosystem I/II; Ph, pheophytin; PQ, plastoquinone; Cytb6f, cytochrome b6/f complex; FD, ferredoxin; FNR; ferredoxin NADP+ reductase; CEF, cyclic electron flow; RuBP, ribulose-1,5-biphosphate; RuBisCO, ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; Asc, ascorbate; MDA, monodehydroascorbate; APx, ascorbate peroxidase; MDAR, monodehydroascorbate reductase; DHA, dehydroascorbate; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; GSH, reduced glutathione; GR, glutathione reductase; DHAR, dehydroascorbate reductase; SAA, systemic acquired acclimation; CWI, cell-wall integrity; GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptors; PLC, phospholipase C; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; InsP3, inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate; CPK, calcium-dependent protein kinase; CBL, calcineurin B-like; CIPK, CBL-interacting protein kinase; SOS, salt overly sensitive; SnRK, SNF1/AMPK-related kinase; ABA, abscisic acid; RbohD/F, respiratory burst oxidase homolog D/F; TFs, transcription factors; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ER–MCS, ER–membrane contact sites; UPR, unfolded protein response; OPF, oxidative protein folding; MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate; MVA, mevalonic acid; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase; DXP, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; MCT; 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase; CD-ME, 4-(cytidine-5′-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol; CMK, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, CD-ME2P, 4-(cytidine-5′-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2-phosphate; MDS, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; ME-cPP, methylerythritol cyclodiphosphate; HDS, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl- diphosphate synthase; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; AACT, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; HMGS, HMG-CoA synthase; HMGR, HMG-CoA reductase; MVA, mevalonate/mevalonic acid; MK, mevalonate kinase; MVP, mevalonate-5-phosphate; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; MVPP, mevalonate pyrpophosphate; MVD, diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; DMAPP, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; IDI, IPP-DMAPP isomerase; PT, prenyl transferase; GPP, geranyl pyrophosphate; FPP, farnesyl pyrophosphate; GGPP, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. Photosynthetic REDOX signals and quenching are an adaptation of [27], while the terpenoid biosynthesis pathway is directly adopted from [28,29].